Protein kinase D1 mediates anchorage-dependent and -independent growth of tumor cells via the zinc finger transcription factor Snail1
- PMID: 22791710
- PMCID: PMC3463335
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.370999
Protein kinase D1 mediates anchorage-dependent and -independent growth of tumor cells via the zinc finger transcription factor Snail1
Abstract
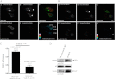
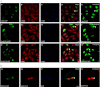
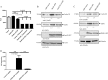
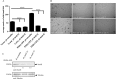
We here identify protein kinase D1 (PKD1) as a major regulator of anchorage-dependent and -independent growth of cancer cells controlled via the transcription factor Snail1. Using FRET, we demonstrate that PKD1, but not PKD2, efficiently interacts with Snail1 in nuclei. PKD1 phosphorylates Snail1 at Ser-11. There was no change in the nucleocytoplasmic distribution of Snail1 using wild type Snail1 and Ser-11 phosphosite mutants in different tumor cells. Regardless of its phosphorylation status or following co-expression of constitutively active PKD, Snail1 was predominantly localized to cell nuclei. We also identify a novel mechanism of PKD1-mediated regulation of Snail1 transcriptional activity in tumor cells. The interaction of the co-repressors histone deacetylases 1 and 2 as well as lysyl oxidase-like protein 3 with Snail1 was impaired when Snail1 was not phosphorylated at Ser-11, which led to reduced Snail1-associated histone deacetylase activity. Additionally, lysyl oxidase-like protein 3 expression was up-regulated by ectopic PKD1 expression, implying a synergistic regulation of Snail1-driven transcription. Ectopic expression of PKD1 also up-regulated proliferation markers such as Cyclin D1 and Ajuba. Accordingly, Snail1 and its phosphorylation at Ser-11 were required and sufficient to control PKD1-mediated anchorage-independent growth and anchorage-dependent proliferation of different tumor cells. In conclusion, our data show that PKD1 is crucial to support growth of tumor cells via Snail1.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Protein kinase D1 (PKD1) phosphorylation on Ser203 by type I p21-activated kinase (PAK) regulates PKD1 localization.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jun 9;292(23):9523-9539. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.771394. Epub 2017 Apr 13. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28408623 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase D1 maintains the epithelial phenotype by inducing a DNA-bound, inactive SNAI1 transcriptional repressor complex.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30459. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030459. Epub 2012 Jan 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22276203 Free PMC article.
-
Biphasic Regulation of Yes-associated Protein (YAP) Cellular Localization, Phosphorylation, and Activity by G Protein-coupled Receptor Agonists in Intestinal Epithelial Cells: A NOVEL ROLE FOR PROTEIN KINASE D (PKD).J Biol Chem. 2016 Aug 19;291(34):17988-8005. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.711275. Epub 2016 Jul 1. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27369082 Free PMC article.
-
Location, location, location: the role of cyclin D1 nuclear localization in cancer.J Cell Biochem. 2005 Dec 1;96(5):906-13. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20613. J Cell Biochem. 2005. PMID: 16163738 Review.
-
Control of Snail1 protein stability by post-translational modifications: the basis for a complex regulation of Snail1 function.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Apr 28;21(7):3183-3196. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.108903. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40384869 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protein kinase D2: a versatile player in cancer biology.Oncogene. 2018 Mar;37(10):1263-1278. doi: 10.1038/s41388-017-0052-8. Epub 2017 Dec 20. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29259300 Review.
-
A time frame permissive for Protein Kinase D2 activity to direct angiogenesis in mouse embryonic stem cells.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 7;5:11742. doi: 10.1038/srep11742. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26148697 Free PMC article.
-
LOXL3 Function Beyond Amino Oxidase and Role in Pathologies, Including Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 23;20(14):3587. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143587. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31340433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Analysis on Prognosis and Immune Infiltration of Lysyl Oxidase Family Members in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma With Experimental Verification.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Apr 1;9:778857. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.778857. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35433829 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase D2 induces invasion of pancreatic cancer cells by regulating matrix metalloproteinases.Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Feb;25(3):324-36. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-06-0334. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24336522 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lint J. V., Rykx A., Vantus T., Vandenheede J. R. (2002) Getting to know protein kinase D. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 34, 577–581 - PubMed
-
- Eiseler T., Schmid M. A., Topbas F., Pfizenmaier K., Hausser A. (2007) PKD is recruited to sites of actin remodelling at the leading edge and negatively regulates cell migration. FEBS Lett. 581, 4279–4287 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

