Longitudinal patterns in physical activity and sedentary behaviour from mid-life to early old age: a substudy of the Whitehall II cohort
- PMID: 22791800
- PMCID: PMC3505863
- DOI: 10.1136/jech-2011-200505
Longitudinal patterns in physical activity and sedentary behaviour from mid-life to early old age: a substudy of the Whitehall II cohort
Abstract
Background: There are few longitudinal data on physical activity patterns from mid-life into older age. The authors examined associations of self-reported physical activity, adiposity and socio-demographic factors in mid-life with objectively assessed measures of activity in older age.
Methods: Participants were 394 healthy men and women drawn from the Whitehall II population-based cohort study. At the baseline assessment in 1997 (mean age 54 years), physical activity was assessed through self-report and quantified as metabolic equivalent of task hours/week. At the follow-up in 2010 (mean age 66 years), physical activity was objectively measured using accelerometers worn during waking hours for seven consecutive days (average daily wear time 891 ± 68 min/day).
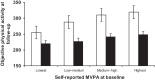
Results: Self-reported physical activity at baseline was associated with objectively assessed activity at follow-up in various activity categories, including light-, moderate- and vigorous-intensity activity (all ps<0.04). Participants in the highest compared with lowest quartile of self-reported activity level at baseline recorded on average 64.1 (95% CI 26.2 to 102.1) counts per minute more accelerometer-assessed activity at follow-up and 9.0 (2.0-16.0) min/day more moderate-to-vigorous daily activity, after adjusting for baseline covariates. Lower education, obesity and self-perceived health status were also related to physical activity at follow-up. Only age and education were associated with objectively measured sedentary time at follow-up.
Conclusion: Physical activity behaviour in middle age was associated with objectively measured physical activity in later life after 13 years of follow-up, suggesting that the habits in adulthood are partly tracked into older age.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Stessman J, Hammerman-Rozenberg R, Cohen A, et al. Physical activity, function, and longevity among the very old. Arch Intern Med 2009;169:1476–83 - PubMed
-
- Hamer M, Chida Y. Physical activity and risk of neurodegenerative disease: a systematic review of prospective evidence. Psychol Med 2009;39:3–11 - PubMed
-
- Garcia AW, Pender NJ, Antonakos CL. Changes in physical activity beliefs and behaviors of boys and girls across the transition to junior high school. J Adolesc Health 1998;22:394–402 - PubMed
-
- Burke V, Beilin LJ, Dunbar D. Changes in health-related behaviours and cardiovascular risk factors in young adults: associations with living with a partner. Prev Med 2004;39:722–30 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
