Effects of chronic nicotine on the autocrine regulation of pancreatic cancer cells and pancreatic duct epithelial cells by stimulatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters
- PMID: 22791813
- PMCID: PMC3514900
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgs229
Effects of chronic nicotine on the autocrine regulation of pancreatic cancer cells and pancreatic duct epithelial cells by stimulatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters
Erratum in
- Carcinogenesis. 2014 Nov;35(11):2630
Abstract
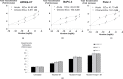
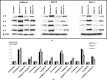
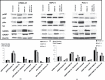
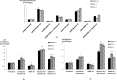
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) has a mortality rate near 100%. Smoking is a documented risk factor. However, the mechanisms of smoking-associated pancreatic carcinogenesis are poorly understood. We have shown that binding of nicotine to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) expressing subunits α7, α3 and α5 in PDAC and pancreatic duct epithelial cells in vitro triggered the production of the neurotransmitters noradrenaline and adrenaline by these cells. In turn, this autocrine catecholamine loop significantly stimulated cell proliferation via cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent signaling downstream of beta-adrenergic receptors. However, the observed responses only represent acute cellular reactions to single doses of nicotine whereas nicotine exposure in smokers is chronic. Using the PDAC cell lines BxPC-3 and Panc-1 and immortalized pancreatic duct epithelial cell line HPDE6-C7, our current experiments reveal a significant sensitization of the nAChR-driven autocrine catecholamine regulatory loop in cells pre-exposed to nicotine for 7 days. The resulting increase in catecholamine production was associated with significant inductions in the phosphorylation of signaling proteins ERK, CREB, Src and AKT, upregulated protein expression of nAChR subunits α3, α4, α5 and α7 and increased responsiveness to nicotine in 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazole-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide and cell migration assays. All three cell lines produced the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid, an activity inhibited by gene knockdown of the α4β2nAChR and suppressed by chronic nicotine via receptor desensitization. All of the observed adverse effects of chronic nicotine were reversed by treatment of the cells with γ-aminobutyric acid, suggesting the potential usefulness of this agent for the improvement of PDAC intervention strategies in smokers.
Figures


References
-
- Silverman D.T., et al. 1994. Cigarette smoking and pancreas cancer: a case-control study based on direct interviews J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 86 1510–1516 - PubMed
-
- Jemal A., et al. 2002. Cancer statistics, 2002 CA Cancer J. Clin. 52 23–47 - PubMed
-
- Chowdhury P., et al. 2008. A cell-based approach to study changes in the pancreas following nicotine exposure in an animal model of injury Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 393 547–555 - PubMed
-
- Gold E.B., et al. 1993. Chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer N. Engl. J. Med. 328 1485–1486 - PubMed
-
- Lin R.S., et al. 1981. A multifactorial model for pancreatic cancer in man. Epidemiologic evidence JAMA. 245 147–152 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

