Suppression of Bmp4 signaling by the zinc-finger repressors Osr1 and Osr2 is required for Wnt/β-catenin-mediated lung specification in Xenopus
- PMID: 22791896
- PMCID: PMC3403107
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.078220
Suppression of Bmp4 signaling by the zinc-finger repressors Osr1 and Osr2 is required for Wnt/β-catenin-mediated lung specification in Xenopus
Abstract
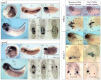
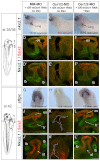
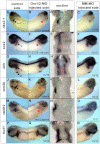
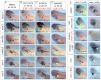
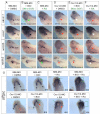
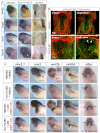
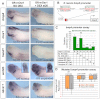
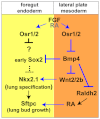
Embryonic development of the respiratory system is regulated by a series of mesenchymal-epithelial interactions that are only partially understood. Mesenchymal FGF and Wnt2/Wnt2b signaling are implicated in specification of mammalian pulmonary progenitors from the ventral foregut endoderm, but their epistatic relationship and downstream targets are largely unknown. In addition, how wnt2 and wnt2b are regulated in the developing foregut mesenchyme is unknown. We show that the Odd-skipped-related (Osr) zinc-finger transcriptional repressors Osr1 and Osr2 are redundantly required for Xenopus lung specification in a molecular pathway linking foregut pattering by FGFs to Wnt-mediated lung specification and RA-regulated lung bud growth. FGF and RA signals are required for robust osr1 and osr2 expression in the foregut endoderm and surrounding lateral plate mesoderm (lpm) prior to respiratory specification. Depletion of both Osr1 and Osr2 (Osr1/Osr2) results in agenesis of the lungs, trachea and esophagus. The foregut lpm of Osr1/Osr2-depleted embryos fails to express wnt2, wnt2b and raldh2, and consequently Nkx2.1(+) progenitors are not specified. Our data suggest that Osr1/Osr2 normally repress bmp4 expression in the lpm, and that BMP signaling negatively regulates the wnt2b domain. These results significantly advance our understanding of early lung development and may impact strategies to differentiate respiratory tissue from stem cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tbx5 drives Aldh1a2 expression to regulate a RA-Hedgehog-Wnt gene regulatory network coordinating cardiopulmonary development.Elife. 2021 Oct 13;10:e69288. doi: 10.7554/eLife.69288. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34643182 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acid-activated Ndrg1a represses Wnt/β-catenin signaling to allow Xenopus pancreas, oesophagus, stomach, and duodenum specification.PLoS One. 2013 May 31;8(5):e65058. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065058. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23741453 Free PMC article.
-
Osr1 functions downstream of Hedgehog pathway to regulate foregut development.Dev Biol. 2017 Jul 1;427(1):72-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.05.005. Epub 2017 May 10. Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28501478 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-catenin signaling in hepatic development and progenitors: which way does the WNT blow?Dev Dyn. 2011 Mar;240(3):486-500. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22522. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Dev Dyn. 2011. PMID: 21337461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-transcriptional regulation in Xenopus embryos: role and targets of EDEN-BP.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Dec;33(Pt 6):1541-3. doi: 10.1042/BST0331541. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16246165 Review.
Cited by
-
Xenopus as a Model for GI/Pancreas Disease.Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2015 Jun 1;3(2):137-145. doi: 10.1007/s40139-015-0076-0. Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26236566 Free PMC article.
-
Multigenerational paternal obesity enhances the susceptibility to male subfertility in offspring via Wt1 N6-methyladenosine modification.Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 14;15(1):1353. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45675-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38355624 Free PMC article.
-
Esophageal Organoids from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Delineate Sox2 Functions during Esophageal Specification.Cell Stem Cell. 2018 Oct 4;23(4):501-515.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.08.008. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Cell Stem Cell. 2018. PMID: 30244869 Free PMC article.
-
Mesodermal lineages in the developing respiratory system.Trends Dev Biol. 2016;9:91-110. Trends Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 34707332 Free PMC article.
-
Odd-skipped related-1 controls neural crest chondrogenesis during tongue development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Nov 12;110(46):18555-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1306495110. Epub 2013 Oct 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24167250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cardoso W. V., Lü J. (2006). Regulation of early lung morphogenesis: questions, facts and controversies. Development 133, 1611–1624 - PubMed
-
- Chen F., Desai T. J., Qian J., Niederreither K., Lü J., Cardoso W. V. (2007). Inhibition of Tgf beta signaling by endogenous retinoic acid is essential for primary lung bud induction. Development 134, 2969–2979 - PubMed
-
- Deimling S. J., Drysdale T. A. (2009). Retinoic acid regulates anterior-posterior patterning within the lateral plate mesoderm of Xenopus. Mech. Dev. 126, 913–923 - PubMed

