Ultra-high resolution optical coherence tomography for monitoring tear meniscus volume in dry eye after topical cyclosporine treatment
- PMID: 22791975
- PMCID: PMC3392922
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S32384
Ultra-high resolution optical coherence tomography for monitoring tear meniscus volume in dry eye after topical cyclosporine treatment
Abstract
Purpose: This study was designed to determine the ability of ultra-high-resolution optical coherence tomography (UHR-OCT) to monitor tear meniscus volume after dry eye treatment with Restasis(®) (0.05% cyclosporine).
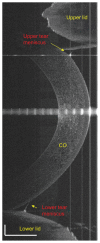
Methods: UHR-OCT was used to image the upper and lower tear menisci (height and volume) in 14 consecutive dry eye patients at baseline. The treatment group was initiated on daily Restasis and measurements were repeated at 1 and 2 months while on treatment. All measurements were performed immediately after a blink.
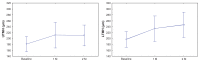
Results: The baseline tear meniscus volumes were 0.40 ± 0.19 μL (upper) and 0.43 ± 0.18 μL (lower). In the treatment group, tear meniscus heights showed significant increases of both upper (post-hoc test with Bonferroni correction: P = 0.003) and lower (P = 0.0003) tear menisci, after 1 month on Restasis. The tear meniscus volumes in the treatment group after 1 month of Restasis showed significant increases of both upper (P = 0.007) and lower (P = 0.007) tear menisci. At 2 months, the increase of the tear meniscus was still evident in all measured variables compared with baseline (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: UHR-OCT offers a promising tool for monitoring dry eye treatment. With this method, a measurable increase in tear meniscus volume was evident after 1 month of treatment with Restasis in dry eye patients.
Keywords: Restasis®; UHR-OCT; dry eye; tear dynamics; tear menisci.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tear meniscus volume in dry eye after punctal occlusion.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Apr;51(4):1965-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-4349. Epub 2009 Nov 20. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 19933200
-
Reduced tear meniscus dynamics in dry eye patients with aqueous tear deficiency.Am J Ophthalmol. 2010 Jun;149(6):932-938.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2010.01.004. Epub 2010 Apr 8. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010. PMID: 20378096 Free PMC article.
-
Upper and lower tear menisci in the diagnosis of dry eye.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009 Jun;50(6):2722-6. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-2704. Epub 2009 Feb 14. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19218609
-
Comparison of two artificial tear formulations for dry eye through high-resolution optical coherence tomography.Clin Exp Optom. 2011 Nov;94(6):549-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1444-0938.2011.00632.x. Epub 2011 Sep 19. Clin Exp Optom. 2011. PMID: 21929716 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of Tear Meniscus Dynamics Using Anterior Segment Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography After Topical Solution Instillation for Dry Eye.Cornea. 2016 May;35(5):654-8. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000000807. Cornea. 2016. PMID: 26989953
Cited by
-
Patients with more severe symptoms of neuropathic ocular pain report more frequent and severe chronic overlapping pain conditions and psychiatric disease.Br J Ophthalmol. 2017 Feb;101(2):227-231. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2015-308214. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Br J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 27130915 Free PMC article.
-
Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography for monitoring the lower tear meniscus in dry eye after acupuncture treatment.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:492150. doi: 10.1155/2015/492150. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 25788963 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Clinical, Diagnostic, and Advanced Imaging Characterization of the Ocular Surface in Spontaneous Aqueous Deficient Dry Eye Disease in Dogs.Cornea. 2019 Dec;38(12):1568-1575. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000002081. Cornea. 2019. PMID: 31369464 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical effectiveness of diquafosol ophthalmic solution 3% in Korean patients with dry eye disease: a multicenter prospective observational study.Int J Ophthalmol. 2021 Oct 18;14(10):1518-1526. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2021.10.07. eCollection 2021. Int J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34667727 Free PMC article.
-
The Development and Clinical Application of Innovative Optical Ophthalmic Imaging Techniques.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 30;9:891369. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.891369. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35847772 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Palakuru J, Wang J, Aquavella J. Effect of blinking on tear dynamics. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48(7):3032–3037. - PubMed
-
- Shen M, Li J, Wang J, et al. Upper and lower tear menisci in the diagnosis of dry eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009;50(6):2722–2726. - PubMed
-
- Chen F, Shen M, Chen W, et al. Tear meniscus volume in dry eye after punctal occlusion. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51(4):1965–1969. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

