Efficacy and safety of fibrin sealant for tissue adherence in facial rhytidectomy
- PMID: 22791995
- PMCID: PMC3391924
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S25747
Efficacy and safety of fibrin sealant for tissue adherence in facial rhytidectomy
Abstract
The purpose of this review is to clarify the present use of fibrin sealant in rhyditectomy procedures and help maximize the appropriate and safe application of this material. A set of terms and definitions for hemostats, sealants, and adhesives based on group, category, and class will be employed to highlight the specific capabilities of fibrin sealant. Fibrin sealant has now emerged as an example of maximizing the usefulness of a surgical agent and is the only product with Food and Drug Administration approval in all three groupings: hemostats; sealants; and adhesives. A variety of manufacturers' fibrin sealant products are available including multiple liquids and one patch. A single liquid product is now specifically indicated for skin flap adherence during rhytidectomy. The unique characteristic of this particular two component fibrin sealant adhesive agent is its slower polymerization rate as a result of a low thrombin concentration which when combined with fibrinogen permits adequate time for manipulation of flaps and tissues prior to final fixation. In addition to its flap adherence and potential space elimination capability, fibrin sealant is also an excellent blood clotting agent and can seal tissues to prevent lymphatic leak or serous fluid accumulation. Thus, it is almost ideally suited to reduce the occurrence of fluid accumulation, hematomas, ecchymoses, and swelling, as well as to possibly eliminate the need for drains following rhytidectomy. A literature review of fibrin sealant in rhytidectomy is included to help define the current state of its clinical use. The author's recommendations for the best use of this material during facial procedures are also provided.
Keywords: adhesives; blood; hemostats; lymph; sealants; serous fluid.
Figures


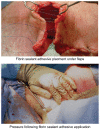

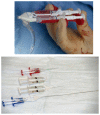
Similar articles
-
Randomized, controlled, phase 3 study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of fibrin sealant VH S/D 4 s-apr (Artiss) to improve tissue adherence in subjects undergoing rhytidectomy.Aesthet Surg J. 2013 May;33(4):487-96. doi: 10.1177/1090820X13479969. Epub 2013 Apr 5. Aesthet Surg J. 2013. PMID: 23563904 Clinical Trial.
-
Fibrin Sealants in Dura Sealing: A Systematic Literature Review.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 27;11(4):e0151533. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151533. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27119993 Free PMC article.
-
State-of-the-art review: Hemostats, sealants, and adhesives II: Update as well as how and when to use the components of the surgical toolbox.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2010 Oct;16(5):497-514. doi: 10.1177/1076029610363589. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2010. PMID: 20699255 Review.
-
In vivo use of human fibrin glue under the subperiosteal and subcutaneous planes in Holtzman rats.Aesthet Surg J. 2003 Nov-Dec;23(6):458-63. doi: 10.1016/j.asj.2003.09.010. Aesthet Surg J. 2003. PMID: 19336116
-
Fibrin sealant: clinical use and the development of the University of Virginia Tissue Adhesive Center.Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2001 Jan;31(1):108-18. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2001. PMID: 11314860 Review.
Cited by
-
A hospital cost analysis of a fibrin sealant patch in soft tissue and hepatic surgical bleeding.Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2016 Sep 21;8:507-519. doi: 10.2147/CEOR.S112762. eCollection 2016. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2016. PMID: 27703386 Free PMC article.
-
Clearing the Smoke: The Evidence behind Risk of Electrocautery Smoke and Mitigation Strategies.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024 Aug 13;12(8):e6039. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000006039. eCollection 2024 Aug. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024. PMID: 39139844 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrin Sealant: The Only Approved Hemostat, Sealant, and Adhesive-a Laboratory and Clinical Perspective.ISRN Surg. 2014 Mar 4;2014:203943. doi: 10.1155/2014/203943. eCollection 2014. ISRN Surg. 2014. PMID: 24729902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Getting to hemostasis: general and thoracic surgical challenges.Tex Heart Inst J. 2012;39(6):868-70. Tex Heart Inst J. 2012. PMID: 23304040 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Health and economic outcomes associated with uncontrolled surgical bleeding: a retrospective analysis of the Premier Perspectives Database.Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2015 Jul 22;7:409-21. doi: 10.2147/CEOR.S86369. eCollection 2015. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2015. PMID: 26229495 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spotnitz WD, Burks S. Hemostats, sealants, and adhesives: components of the surgical toolbox. Transfusion. 2008;48(7):1502–1516. - PubMed
-
- Spotnitz WD, Burks S. State-of-the-art review: Hemostats, sealants, and adhesives II: Update as well as how and when to use the components of the surgical toolbox. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2010;16(5):497–514. - PubMed
-
- Spotnitz WD, Burks S. Hemostats, sealants, and adhesives III: A new update as well as cost and regulatory considerations for components of the surgical toolbox. Transfusion. 2012 In press. - PubMed
-
- Wang GJ, Goldthwaite CA, Jr, Burks SG, Spotnitz WD Orthopaedic Research Group. Experience improves successful use of fibrin sealant in total knee arthroplasty: implications for surgical education. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2003;13(5):389–397. - PubMed
-
- Spotnitz WD. Fibrin sealant: past, present, and future: a brief review. World J Surg. 2010;34(4):632–634. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

