IL-1beta signals through the EGF receptor and activates Egr-1 through MMP-ADAM
- PMID: 22792188
- PMCID: PMC3391205
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039811
IL-1beta signals through the EGF receptor and activates Egr-1 through MMP-ADAM
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2013;8(12). doi:10.1371/annotation/a0bc2cbb-0390-4476-833d-30ce4f829794
Abstract
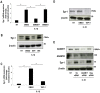
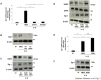
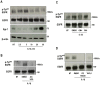
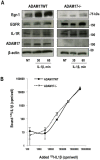
The immediate-early gene Egr-1 controls the inducible expression of many genes implicated in the pathogenesis of a range of vascular disorders, yet our understanding of the mechanisms controlling the rapid expression of this prototypic zinc finger transcription factor is poor. Here we show that Egr-1 expression induced by IL-1beta is dependent on metalloproteinases (MMP) and a disintegrin and a metalloproteinase (ADAM). Pharmacologic MMP/ADAM inhibitors and siRNA knockdown prevent IL-1beta induction of Egr-1. Further, IL-1beta activates Egr-1 via the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). This is blocked by EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition and EGFR knockdown. IL-1beta induction of Egr-1 expression is reduced in murine embryonic fibroblasts (mEFs) deficient in ADAM17 despite unbiased expression of EGFR and IL-1RI in ADAM17-deficient and wild-type mEFs. Finally, we show that IL-1beta-inducible wound repair after mechanical injury requires both EGFR and MMP/ADAM. This study reports for the first time that Egr-1 induction by IL-1beta involves EGFR and MMP/ADAM-dependent EGFR phosphorylation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cell migration in response to the amino-terminal fragment of urokinase requires epidermal growth factor receptor activation through an ADAM-mediated mechanism.J Vasc Surg. 2009 May;49(5):1296-303. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2008.12.026. J Vasc Surg. 2009. PMID: 19394555 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-induced epidermal growth factor activation in vascular smooth muscle cells is ADAM-dependent.Surgery. 2008 Aug;144(2):245-51. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2008.03.023. Epub 2008 May 27. Surgery. 2008. PMID: 18656632 Free PMC article.
-
Protease-mediated human smooth muscle cell proliferation by urokinase requires epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation by triple membrane signaling.J Surg Res. 2014 Dec;192(2):254-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.06.054. Epub 2014 Jul 2. J Surg Res. 2014. PMID: 25082749 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the activity, differential expression, mutual regulation, and functions of matrix metalloproteinases and a disintegrin and metalloproteinases in hypertension and cardiac disease.J Vasc Res. 2013;50(1):52-68. doi: 10.1159/000345240. Epub 2012 Nov 17. J Vasc Res. 2013. PMID: 23172306 Review.
-
Key metalloproteinase-mediated pathways in the kidney.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021 Aug;17(8):513-527. doi: 10.1038/s41581-021-00415-5. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33879883 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune Responses to IAV Infection and the Roles of L-Selectin and ADAM17 in Lymphocyte Homing.Pathogens. 2022 Jan 25;11(2):150. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11020150. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35215094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decorin mimic inhibits vascular smooth muscle proliferation and migration.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 22;8(11):e82456. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082456. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24278482 Free PMC article.
-
The tribology of cartilage: Mechanisms, experimental techniques, and relevance to translational tissue engineering.Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2020 Oct;79:104880. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2019.10.016. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2020. PMID: 31676140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-1β Induces Tissue Factor Expression in A549 Cells via EGFR-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 21;22(12):6606. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126606. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34205482 Free PMC article.
-
LDL-Dependent Regulation of TNFα/PGE2 Induced COX-2/mPGES-1 Expression in Human Macrophage Cell Lines.Inflammation. 2023 Jun;46(3):893-911. doi: 10.1007/s10753-022-01778-y. Epub 2023 Jan 4. Inflammation. 2023. PMID: 36598592 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Campbell GR, Campbell JH. Smooth muscle phenotypic changes in arterial wall homeostasis: implications for the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Exp Mol Pathol. 1985;42:139–162. - PubMed
-
- Owens GK, Kumar MS, Wamhoff BR. Molecular regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation in development and disease. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:767–801. - PubMed
-
- Gashler A, Sukhatme V. Early growth response protein 1 (Egr-1): prototype of a zinc-finger family of transcription factors. Prog Nucl Acid Res. 1995;50:191–224. - PubMed
-
- Khachigian LM. Early growth response-1 in cardiovascular pathobiology. Circ Res. 2006;98:186–191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

