Screening of 71 P. multocida proteins for protective efficacy in a fowl cholera infection model and characterization of the protective antigen PlpE
- PMID: 22792202
- PMCID: PMC3390355
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039973
Screening of 71 P. multocida proteins for protective efficacy in a fowl cholera infection model and characterization of the protective antigen PlpE
Abstract
Background: There is a strong need for a recombinant subunit vaccine against fowl cholera. We used a reverse vaccinology approach to identify putative secreted or cell surface associated P. multocida proteins that may represent potential vaccine candidate antigens.
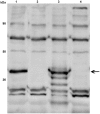
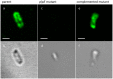
Principal findings: A high-throughput cloning and expression protocol was used to express and purify 71 recombinant proteins for vaccine trials. Of the 71 proteins tested, only one, PlpE in denatured insoluble form, protected chickens against fowl cholera challenge. PlpE also elicited comparable levels of protection in mice. PlpE was localized by immunofluorescence to the bacterial cell surface, consistent with its ability to elicit a protective immune response. To explore the role of PlpE during infection and immunity, a plpE mutant was generated. The plpE mutant strain retained full virulence for mice.
Conclusion: These studies show that PlpE is a surface exposed protein and was the only protein of 71 tested that was able to elicit a protective immune response. However, PlpE is not an essential virulence factor. This is the first report of a denatured recombinant protein stimulating protection against fowl cholera.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Hansson M, Nygren PA, Stahl S. Design and production of recombinant subunit vaccines. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 32 (Pt. 2000;2):95–107. - PubMed
-
- Pizza M, Scarlato V, Masignani V, Giuliani MM, Arico B, et al. Identification of vaccine candidates against serogroup B meningococcus by whole-genome sequencing. Science. 2000;287:1816–1820. - PubMed
-
- Ross BC, Czajkowski L, Hocking D, Margetts M, Webb E, et al. Identification of vaccine candidate antigens from a genomic analysis of Porphyromonas gingivalis. Vaccine. 2001;19:4135–4142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

