Milk matters: soluble Toll-like receptor 2 (sTLR2) in breast milk significantly inhibits HIV-1 infection and inflammation
- PMID: 22792230
- PMCID: PMC3391222
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040138
Milk matters: soluble Toll-like receptor 2 (sTLR2) in breast milk significantly inhibits HIV-1 infection and inflammation
Abstract
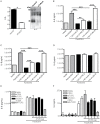
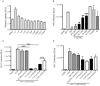
The majority of infants who breastfeed from their HIV-positive mothers remain uninfected despite constant and repeated exposure to virus over weeks to years. This phenomenon is not fully understood but has been closely linked to innate factors in breast milk (BM). Most recently we have focused on one such innate factor, soluble Toll-like receptor 2 (sTLR2) for its significant contribution as an inhibitor of inflammation triggered by bacterial and viral antigens. We hypothesized that sTLR2 in BM inhibits immune activation/inflammation and HIV-1 infection. sTLR2 protein profiles were analyzed in HIV-uninfected BM and showed dramatic variability in expression concentration and predominant sTLR2 forms between women. sTLR2 immunodepleted BM, versus mock-depleted BM, incubated with Pam(3)CSK(4) lead to significant increases in IL-8 production in a TLR2-dependant fashion in U937, HEK293-TLR2, and Caco-2. Importantly, TLR2-specific polyclonal and monoclonal antibody addition to BM prior to cell-free R5 HIV-1 addition led to significantly (P<0.01, P<0.001, respectively) increased HIV-1 infection in TZM-bl reporter cells. To confirm these findings, sTLR2-depletion in BM led to significantly (P<0.001) increased HIV-1 infection in TZM-bl cells. Notably, immunodepletion does not allow for the complete removal of sTLR2 from BM, thus functional testing shown here may underestimate the total effect elicited by sTLR2 against HIV-1 and synthetic bacterial ligand. This study provides evidence for the first time that sTLR2 in BM may provide a dual protective role for infants breastfeeding from their HIV-infected mothers by; (1) immunomodulating pro-inflammatory responses to bacterial ligands, and (2) directly inhibiting cell-free HIV-1 infection. Thus, sTLR2 in BM may be critical to infant health and prove beneficial in decreasing vertical HIV-1 transmission to infants.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Grulee CG, Sanford HN, Schwartz H. Breast and Artificially Fed Infants. Jour AMA. 1935. pp. 1–3.
-
- Beaudry M, Dufour R, Marcoux S. Relation between infant feeding and infections during the first six months of life. J Pediatr. 1995;126:191–197. - PubMed
-
- Kramer MS. “Breast is best”: The evidence. Early Hum Dev. 2010;86:729–732. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2010.08.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arifeen S, Black RE, Antelman G, Baqui A, Caulfield L, et al. Exclusive breastfeeding reduces acute respiratory. 2001. pp. 1–10. doi: 10.1542/peds.108.4.e67. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Coovadia HM, Rollins NC, Bland RM, Little K, Coutsoudis A, et al. Mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 infection during exclusive breastfeeding in the first 6 months of life: an intervention cohort study. Lancet. 2007;369:1107–1116. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60283-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

