Cytochrome b5 and cytokeratin 17 are biomarkers in bronchoalveolar fluid signifying onset of acute lung injury
- PMID: 22792238
- PMCID: PMC3391234
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040184
Cytochrome b5 and cytokeratin 17 are biomarkers in bronchoalveolar fluid signifying onset of acute lung injury
Abstract
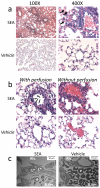
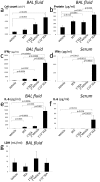
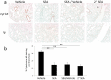
Acute lung injury (ALI) is characterized by pulmonary edema and acute inflammation leading to pulmonary dysfunction and potentially death. Early medical intervention may ameliorate the severity of ALI, but unfortunately, there are no reliable biomarkers for early diagnosis. We screened for biomarkers in a mouse model of ALI. In this model, inhalation of S. aureus enterotoxin A causes increased capillary permeability, cell damage, and increase protein and cytokine concentration in the lungs. We set out to find predictive biomarkers of ALI in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid before the onset of clinical manifestations. A cutting edge proteomic approach was used to compare BAL fluid harvested 16 h post S. aureus enterotoxin A inhalation versus BAL fluid from vehicle alone treated mice. The proteomic PF 2D platform permitted comparative analysis of proteomic maps and mass spectrometry identified cytochrome b5 and cytokeratin 17 in BAL fluid of mice challenged with S. aureus enterotoxin A. Validation of cytochrome b5 showed tropic expression in epithelial cells of the bronchioles. Importantly, S. aureus enterotoxin A inhalation significantly decreased cytochrome b5 during the onset of lung injury. Validation of cytokeratin 17 showed ubiquitous expression in lung tissue and increased presence in BAL fluid after S. aureus enterotoxin A inhalation. Therefore, these new biomarkers may be predictive of ALI onset in patients and could provide insight regarding the basis of lung injury and inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Therapeutic blockade of CD54 attenuates pulmonary barrier damage in T cell-induced acute lung injury.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017 Jul 1;313(1):L177-L191. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00050.2017. Epub 2017 May 4. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28473322 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE) is an indicator of direct lung injury in models of experimental lung injury.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Jul;297(1):L1-5. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.90546.2008. Epub 2009 May 1. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19411309 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of porcine bronchoalveolar fluid-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in a pig model of LPS-induced ALI.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jul;233(7):5447-5457. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26397. Epub 2018 Jan 19. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29231967 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers in acute lung injury.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2015 Apr;209:52-8. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2014.10.006. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25466727 Review.
-
Biomarkers in acute lung injury.Transl Res. 2012 Apr;159(4):205-17. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2012.01.007. Epub 2012 Feb 7. Transl Res. 2012. PMID: 22424425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Toxin Disrupts Endothelial-Cell Tight Junctions via Acid Sphingomyelinase and Ceramide.Infect Immun. 2017 Dec 19;86(1):e00606-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00606-17. Print 2018 Jan. Infect Immun. 2017. PMID: 29084896 Free PMC article.
-
The proteome of Hypobaric Induced Hypoxic Lung: Insights from Temporal Proteomic Profiling for Biomarker Discovery.Sci Rep. 2015 May 29;5:10681. doi: 10.1038/srep10681. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26022216 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen-specific downregulation of miR-150 in CD4 T cells promotes cell survival.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 27;14:1102403. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1102403. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36817480 Free PMC article.
-
Small Airway Susceptibility to Chemical and Particle Injury.Respiration. 2022;101(3):321-333. doi: 10.1159/000519344. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Respiration. 2022. PMID: 34649249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mast cell stabilization alleviates acute lung injury after orthotopic autologous liver transplantation in rats by downregulating inflammation.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 8;8(10):e75262. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075262. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24116032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuebler WM. Biomarkers of acute respiratory distress syndrome: Do good things lie nearby? Crit Care Med. 2011;39:207–209. - PubMed
-
- Gaggar A, Olman MA. Biologic markers of mortality in acute lung injury. Clin Chim Acta. 2006;372:24–32. - PubMed
-
- Thomas D, Chou S, Dauwalder O, Lina G. Diversity in Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2007;93:24–41. - PubMed
-
- Iscimen R, Cartin-Ceba R, Yilmaz M, Khan H, Hubmayr RD, et al. Risk factors for the development of acute lung injury in patients with septic shock: an observational cohort study. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:1518–1522. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

