A Lon-like protease with no ATP-powered unfolding activity
- PMID: 22792246
- PMCID: PMC3391209
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040226
A Lon-like protease with no ATP-powered unfolding activity
Abstract
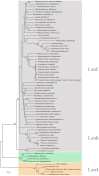
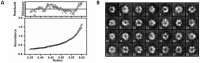
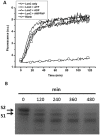
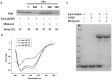
Lon proteases are a family of ATP-dependent proteases involved in protein quality control, with a unique proteolytic domain and an AAA(+) (ATPases associated with various cellular activities) module accommodated within a single polypeptide chain. They were classified into two types as either the ubiquitous soluble LonA or membrane-inserted archaeal LonB. In addition to the energy-dependent forms, a number of medically and ecologically important groups of bacteria encode a third type of Lon-like proteins in which the conserved proteolytic domain is fused to a large N-terminal fragment lacking canonical AAA(+) motifs. Here we showed that these Lon-like proteases formed a clade distinct from LonA and LonB. Characterization of one such Lon-like protease from Meiothermus taiwanensis indicated that it formed a hexameric assembly with a hollow chamber similar to LonA/B. The enzyme was devoid of ATPase activity but retained an ability to bind symmetrically six nucleotides per hexamer; accordingly, structure-based alignment suggested possible existence of a non-functional AAA-like domain. The enzyme degraded unstructured or unfolded protein and peptide substrates, but not well-folded proteins, in ATP-independent manner. These results highlight a new type of Lon proteases that may be involved in breakdown of excessive damage or unfolded proteins during stress conditions without consumption of energy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Sauer RT, Baker TA. AAA+ proteases: ATP-fueled machines of protein destruction. Ann. Review Biochem. 80, 587–612. 2011. - PubMed
-
- Neuwald AF, Aravind L, Spouge JL, Koonin EV. AAA+: A class of chaperone-like ATPases associated with the assembly, operation, and disassembly of protein complexes. Genome Res. 9, 27–43. 1999. - PubMed
-
- Tsilibaris V, Maenhaut-Michel G, Van Melderen L. Biological roles of the Lon ATP-dependent protease. Res. Microbiol. 157, 701–713. 2006. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg AL, Moerschell RP, Chung CH, Maurizi MR. ATP-dependent protease La (lon) from Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 244, 350–375. 1994. - PubMed
-
- Amerik A, Antonov VK, Gorbalenya AE, Kotova SA, Rotanova TV, et al. Site-directed mutagenesis of La protease. A catalytically active serine residue. FEBS. Lett. 287, 211–214. 1991. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

