Calcitonin inhibits SDCP-induced osteoclast apoptosis and increases its efficacy in a rat model of osteoporosis
- PMID: 22792258
- PMCID: PMC3391248
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040272
Calcitonin inhibits SDCP-induced osteoclast apoptosis and increases its efficacy in a rat model of osteoporosis
Abstract
Introduction: Treatment for osteoporosis commonly includes the use of bisphosphonates. Serious side effects of these drugs are caused by the inhibition of bone resorption as a result of osteoclast apoptosis. Treatment using calcitonin along with bisphosphonates overcomes these side-effects in some patients. Calcitonin is known to inhibit bone resorption without reducing the number of osteoclasts and is thought to prolong osteoclast survival through the inhibition of apoptosis. Further understanding of how calcitonin inhibits apoptosis could prove useful to the development of alternative treatment regimens for osteoporosis. This study aimed to analyze the mechanism by which calcitonin influences osteoclast apoptosis induced by a bisphosphate analog, sintered dicalcium pyrophosphate (SDCP), and to determine the effects of co-treatment with calcitonin and SDCP on apoptotic signaling in osteoclasts.
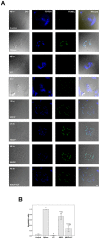
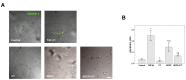
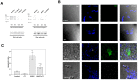
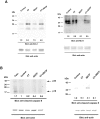
Methods: Isolated osteoclasts were treated with CT, SDCP or both for 48 h. Osteoclast apoptosis assays, pit formation assays, and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining were performed. Using an osteoporosis rat model, ovariectomized (OVX) rats received calcitonin, SDCP, or calcitonin + SDCP. The microarchitecture of the fifth lumbar trabecular bone was investigated, and histomorphometric and biochemical analyses were performed.
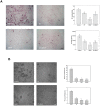
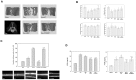
Results: Calcitonin inhibited SDCP-induced apoptosis in primary osteoclast cultures, increased Bcl-2 and Erk activity, and decreased Mcl-1 activity. Calcitonin prevented decreased osteoclast survival but not resorption induced by SDCP. Histomorphometric analysis of the tibia revealed increased bone formation, and microcomputed tomography of the fifth lumbar vertebrate showed an additive effect of calcitonin and SDCP on bone volume. Finally, analysis of the serum bone markers CTX-I and P1NP suggests that the increased bone volume induced by co-treatment with calcitonin and SDCP may be due to decreased bone resorption and increased bone formation.
Conclusions: Calcitonin reduces SDCP-induced osteoclast apoptosis and increases its efficacy in an in vivo model of osteoporosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Rogers MJ, Frith JC, Luckman SP, Coxon FP, Benford HL, et al. Molecular mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates. Bone. 1999;24:73S–79S. - PubMed
-
- Rogers MJ, Crockett JC, Coxon FP, Mönkkönen J. Biochemical and molecular mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates. Bone. 2011;49:34–41. - PubMed
-
- Luckman SP, Hughes DE, Coxon FP, Graham R, Russell G, et al. Nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates inhibit the mevalonate pathway and prevent post-translational prenylation of GTP-binding proteins, including Ras. J Bone Miner Res. 1998;13:581–589. - PubMed
-
- Karsdal MA, Henriksen K, Arnold M, Christiansen C. Calcitonin: a drug of the past or for the future? Physiologic inhibition of bone resorption while sustaining osteoclast numbers improves bone quality. BioDrugs. 2008;22:137–144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

