High-affinity target binding engineered via fusion of a single-domain antibody fragment with a ligand-tailored SH3 domain
- PMID: 22792285
- PMCID: PMC3390362
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040331
High-affinity target binding engineered via fusion of a single-domain antibody fragment with a ligand-tailored SH3 domain
Abstract
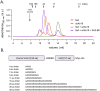
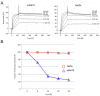
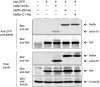
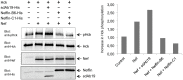
Monoclonal and recombinant antibodies are ubiquitous tools in diagnostics, therapeutics, and biotechnology. However, their biochemical properties lack optimal robustness, their bacterial production is not easy, and possibilities to create multifunctional fusion proteins based on them are limited. Moreover, the binding affinities of antibodies towards their antigens are suboptimal for many applications where they are commonly used. To address these issues we have made use of the concept of creating high binding affinity based on multivalent target recognition via exploiting some of the best features of immunoglobulins (Ig) and non-Ig-derived ligand-binding domains. We have constructed a small protein, named Neffin, comprised of a 118 aa llama Ig heavy chain variable domain fragment (VHH) fused to a ligand-tailored 57 aa SH3 domain. Neffin could be readily produced in large amounts (>18 mg/L) in the cytoplasm of E. coli, and bound with a subpicomolar affinity (K(d) 0.54 pM) to its target, the HIV-1 Nef protein. When expressed in human cells Neffin could potently inhibit Nef function. Similar VHH-SH3 fusion proteins could be targeted against many other proteins of interest and could have widespread use in diverse medical and biotechnology applications where biochemical robustness and strong binding affinity are required.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Single-domain antibody-SH3 fusions for efficient neutralization of HIV-1 Nef functions.J Virol. 2012 May;86(9):4856-67. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06329-11. Epub 2012 Feb 15. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22345475 Free PMC article.
-
Competitive displacement of full-length HIV-1 Nef from the Hck SH3 domain by a high-affinity artificial peptide.Biol Chem. 2007 Jun;388(6):611-5. doi: 10.1515/BC.2007.075. Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17552908
-
SH3 domains with high affinity and engineered ligand specificities targeted to HIV-1 Nef.J Mol Biol. 1999 Nov 12;293(5):1097-106. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3225. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10547288
-
Structure, function, and inhibitor targeting of HIV-1 Nef-effector kinase complexes.J Biol Chem. 2020 Oct 30;295(44):15158-15171. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.012317. Epub 2020 Aug 29. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32862141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reading between the lines: SH3 recognition of an intact protein.Structure. 1996 Jun 15;4(6):657-9. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00071-8. Structure. 1996. PMID: 8805558 Review.
Cited by
-
The Protective Effect of a Long-Acting and Multi-Target HM-3-Fc Fusion Protein in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 10;19(9):2683. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092683. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30201867 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical potential of circulating tumor cells; the need to incorporate a modern "immunological cocktail" in the assay.Cancers (Basel). 2013 Dec 13;5(4):1739-47. doi: 10.3390/cancers5041739. Cancers (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24351672 Free PMC article.
-
Large-Scale Production of Anti-RNase A VHH Expressed in pyrG Auxotrophic Aspergillus oryzae.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 May 31;45(6):4778-4795. doi: 10.3390/cimb45060304. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37367053 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the genetic diversity and population structure of Turkish bread wheat germplasm using iPBS-retrotransposons markers.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Oct;48(10):6739-6748. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06670-w. Epub 2021 Sep 4. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34480687
-
HIV-Nef and ADAM17-Containing Plasma Extracellular Vesicles Induce and Correlate with Immune Pathogenesis in Chronic HIV Infection.EBioMedicine. 2016 Apr;6:103-113. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.03.004. Epub 2016 Mar 3. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27211553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kohler G, Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975;256:495–497. - PubMed
-
- Nelson AL, Dhimolea E, Reichert JM. Development trends for human monoclonal antibody therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:767–774. - PubMed
-
- Holliger P, Hudson PJ. Engineered antibody fragments and the rise of single domains. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23:1126–1136. - PubMed
-
- Pluckthun A, Pack P. New protein engineering approaches to multivalent and bispecific antibody fragments. Immunotechnology. 1997;3:83–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

