Functional analysis of Plasmodium vivax dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase genes through stable transformation of Plasmodium falciparum
- PMID: 22792308
- PMCID: PMC3392216
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040416
Functional analysis of Plasmodium vivax dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase genes through stable transformation of Plasmodium falciparum
Abstract
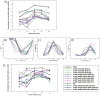
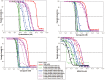
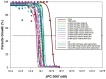
Mechanisms of drug resistance in Plasmodium vivax have been difficult to study partially because of the difficulties in culturing the parasite in vitro. This hampers monitoring drug resistance and research to develop or evaluate new drugs. There is an urgent need for a novel method to study mechanisms of P. vivax drug resistance. In this paper we report the development and application of the first Plasmodium falciparum expression system to stably express P. vivax dhfr-ts alleles. We used the piggyBac transposition system for the rapid integration of wild-type, single mutant (117N) and quadruple mutant (57L/58R/61M/117T) pvdhfr-ts alleles into the P. falciparum genome. The majority (81%) of the integrations occurred in non-coding regions of the genome; however, the levels of pvdhfr transcription driven by the P. falciparum dhfr promoter were not different between integrants of non-coding and coding regions. The integrated quadruple pvdhfr mutant allele was much less susceptible to antifolates than the wild-type and single mutant pvdhfr alleles. The resistance phenotype was stable without drug pressure. All the integrated clones were susceptible to the novel antifolate JPC-2067. Therefore, the piggyBac expression system provides a novel and important tool to investigate drug resistance mechanisms and gene functions in P. vivax.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Defining the role of mutations in Plasmodium vivax dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase gene using an episomal Plasmodium falciparum transfection system.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Sep;54(9):3927-32. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00628-10. Epub 2010 Jun 21. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20566761 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic Plasmodium parasites stably expressing Plasmodium vivax dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase as in vitro and in vivo models for antifolate screening.Malar J. 2011 Oct 7;10:291. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-10-291. Malar J. 2011. PMID: 21981896 Free PMC article.
-
Change in mutation patterns of Plasmodium vivax dihydrofolate reductase (Pvdhfr) and dihydropteroate synthase (Pvdhps) in P. vivax isolates from malaria endemic areas of Thailand.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2011 Aug;106 Suppl 1:130-3. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02762011000900017. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2011. PMID: 21881767
-
Phylogenetic analysis suggests single and multiple origins of dihydrofolate reductase mutations in Plasmodium vivax.Acta Trop. 2021 Mar;215:105821. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2020.105821. Epub 2021 Jan 3. Acta Trop. 2021. PMID: 33406444 Review.
-
The dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthetase gene in the drug resistance of malaria parasites.Pharmacol Ther. 1990;48(1):45-59. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90017-v. Pharmacol Ther. 1990. PMID: 2274577 Review.
Cited by
-
Next-Generation Sequencing of Plasmodium vivax Patient Samples Shows Evidence of Direct Evolution in Drug-Resistance Genes.ACS Infect Dis. 2015 Aug 14;1(8):367-79. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.5b00049. Epub 2015 Aug 3. ACS Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26719854 Free PMC article.
-
Editing the Plasmodium vivax genome, using zinc-finger nucleases.J Infect Dis. 2015 Jan 1;211(1):125-9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu423. Epub 2014 Jul 31. J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25081932 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing Research Models and Technologies to Overcome Biological Barriers to Plasmodium vivax Control.Trends Parasitol. 2018 Feb;34(2):114-126. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2017.10.009. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Trends Parasitol. 2018. PMID: 29153587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of two methods for transformation of Plasmodium knowlesi: Direct schizont electroporation and spontaneous plasmid uptake from plasmid-loaded red blood cells.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2017 Dec;218:16-22. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2017.10.001. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2017. PMID: 28988930 Free PMC article.
-
Antimalarial potential of compounds isolated from Mammea siamensis T. Anders. flowers: in vitro and molecular docking studies.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Oct 12;22(1):266. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03742-7. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 36224571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mendis K, Sina BJ, Marchesini P, Carter R. The neglected burden of Plasmodium vivax malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001;64:97–106. - PubMed
-
- Mueller I, Galinski MR, Baird JK, Carlton JM, Kochar DK, et al. Key gaps in the knowledge of Plasmodium vivax, a neglected human malaria parasite. The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 2009;9:555–566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

