Small ribosomal protein RPS0 stimulates translation initiation by mediating 40S-binding of eIF3 via its direct contact with the eIF3a/TIF32 subunit
- PMID: 22792338
- PMCID: PMC3390373
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040464
Small ribosomal protein RPS0 stimulates translation initiation by mediating 40S-binding of eIF3 via its direct contact with the eIF3a/TIF32 subunit
Abstract
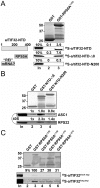
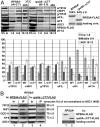
The ribosome translates information encoded by mRNAs into proteins in all living cells. In eukaryotes, its small subunit together with a number of eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs) is responsible for locating the mRNA's translational start to properly decode the genetic message that it carries. This multistep process requires timely and spatially coordinated placement of eIFs on the ribosomal surface. In our long-standing pursuit to map the 40S-binding site of one of the functionally most complex eIFs, yeast multisubunit eIF3, we identified several interactions that placed its major body to the head, beak and shoulder regions of the solvent-exposed side of the 40S subunit. Among them is the interaction between the N-terminal domain (NTD) of the a/TIF32 subunit of eIF3 and the small ribosomal protein RPS0A, residing near the mRNA exit channel. Previously, we demonstrated that the N-terminal truncation of 200 residues in tif32-Δ8 significantly reduced association of eIF3 and other eIFs with 40S ribosomes in vivo and severely impaired translation reinitiation that eIF3 ensures. Here we show that not the first but the next 200 residues of a/TIF32 specifically interact with RPS0A via its extreme C-terminal tail (CTT). Detailed analysis of the RPS0A conditional depletion mutant revealed a marked drop in the polysome to monosome ratio suggesting that the initiation rates of cells grown under non-permissive conditions were significantly impaired. Indeed, amounts of eIF3 and other eIFs associated with 40S subunits in the pre-initiation complexes in the RPS0A-depleted cells were found reduced; consistently, to the similar extent as in the tif32-Δ8 cells. Similar but less pronounced effects were also observed with the viable CTT-less mutant of RPS0A. Together we conclude that the interaction between the flexible RPS0A-CTT and the residues 200-400 of the a/TIF32-NTD significantly stimulates attachment of eIF3 and its associated eIFs to small ribosomal subunits in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

