Establishment and characterization of a buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) mammary epithelial cell line
- PMID: 22792341
- PMCID: PMC3392245
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040469
Establishment and characterization of a buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) mammary epithelial cell line
Abstract
Background: The objective of this study was to establish the buffalo mammary epithelial cell line (BuMEC) and characterize its mammary specific functions.
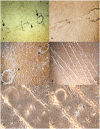
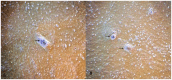
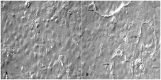
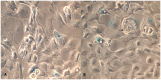
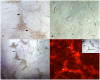
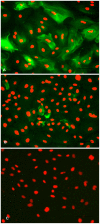
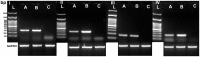
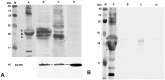
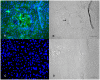
Methodology: Buffalo mammary tissue collected from the slaughter house was processed enzymatically to obtain a heterogenous population of cells containing both epithelial and fibroblasts cells. Epithelial cells were purified by selective trypsinization and were grown in a plastic substratum. The purified mammary epithelial cells (MECs) after several passages were characterized for mammary specific functions by immunocytochemistry, RT-PCR and western blot.
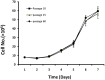
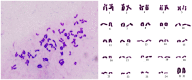
Principal findings: The established buffalo mammary epithelial cell line (BuMEC) exhibited epithelial cell characteristics by immunostaining positively with cytokeratin 18 and negatively with vimentin. The BuMEC maintained the characteristics of its functional differentiation by expression of β-casein, κ-casein, butyrophilin and lactoferrin. BuMEC had normal growth properties and maintained diploid chromosome number (2n = 50) before and after cryopreservation. A spontaneously immortalized buffalo mammary epithelial cell line was established after 20 passages and was continuously subcultured for more than 60 passages without senescence.
Conclusions: We have established a buffalo mammary epithelial cell line that can be used as a model system for studying mammary gland functions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
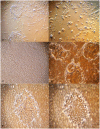
References
-
- “Water Buffalo An asset undervalued”. United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization. Retrieved on 2011–09–15. 2000. FAO website: http://www.aphca.org/publications/files/w_buffalo.pdf.
-
- Martinet J, Houdebine LM, Head HH. Biology of Lactation. Paris: INRA publication. 670 p. 1999.
-
- Larson BL. Larson BL, Anderson, RR, editors. Biosynthesis and cellular secretion of milk. 1985. pp. 129–163. Lactation. Ames: The lowa State University Press.
-
- Rosen JM, Jones WK, Campbell SM, Bisbee CA, Yu-Lee LY. Czech MP, Kahn, CR, editors. Structure and regulation of peptide hormone responsive genes. Vol 23. 1985. New York: A. R. Liss. Proceedings UCLA Symposium on Membrane Receptors and Cellular Regulation. (385–396).
-
- Levine JF, Stockdale FE. 3T3-L1 adipocytes promote the growth of mammary epithelium. Exp Cell Res. 1984;151:112–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

