CD154 blockade alters innate immune cell recruitment and programs alloreactive CD8+ T cells into KLRG-1(high) short-lived effector T cells
- PMID: 22792369
- PMCID: PMC3390379
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040559
CD154 blockade alters innate immune cell recruitment and programs alloreactive CD8+ T cells into KLRG-1(high) short-lived effector T cells
Abstract
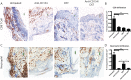
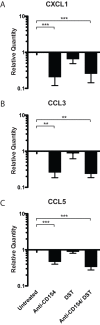
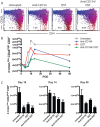
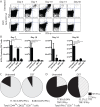
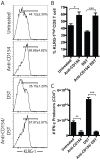
CD154/CD40 blockade combined with donor specific transfusion remains one of the most effective therapies in prolonging allograft survival. Despite this, the mechanisms by which these pathways synergize to prevent rejection are not completely understood. Utilizing a BALB/c (H2-K(d)) to B6 (H2-K(b)) fully allogeneic skin transplant model system, we performed a detailed longitudinal analysis of the kinetics and magnitude of CD8(+) T cell expansion and differentiation in the presence of CD154/CD40 pathway blockade. Results demonstrated that treatment with anti-CD154 vs. DST had distinct and opposing effects on activated CD44(high) CD62L(low) CD8(+) T cells in skin graft recipients. Specifically, CD154 blockade delayed alloreactive CD8(+) T cell responses, while DST accelerated them. DST inhibited the differentiation of alloreactive CD8(+) T cells into multi-cytokine producing effectors, while CD40/CD154 blockade led to the diminution of the KLRG-1(low) long-lived memory precursor population compared with either untreated or DST treated animals. Moreover, only CD154 blockade effectively inhibited CXCL1 expression and neutrophil recruitment into the graft. When combined, anti-CD154 and DST acted synergistically to profoundly diminish the absolute number of IFN-γ producing alloreactive CD8(+) T cells, and intra-graft expression of inflammatory chemokines. These findings demonstrate that the previously described ability of anti-CD154 and DST to result in alloreactive T cell deletion involves both delayed kinetics of T cell expansion and differentiation and inhibited development of KLRG-1(low) memory precursor cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Halloran PF. Immunosuppressive drugs for kidney transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2715–2729. - PubMed
-
- Larsen CP, Elwood ET, Alexander DZ, Ritchie SC, Hendrix R, et al. Long-term acceptance of skin and cardiac allografts after blocking CD40 and CD28 pathways. Nature. 1996;381:434–438. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Andrews D, Colvin RB, Sachs DH, Cosimi AB. Thromboembolic complications after treatment with monoclonal antibody against CD40 ligand. Nat Med. 2000;6:114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

