IL-15 expression on RA synovial fibroblasts promotes B cell survival
- PMID: 22792388
- PMCID: PMC3392224
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040620
IL-15 expression on RA synovial fibroblasts promotes B cell survival
Abstract
Introduction: The purpose of this study was to examine the role of RA Synovial Fibroblast (RASFib) IL-15 expression on B cell survival.
Methods: Magnetically sorted peripheral blood memory B cells from 15 healthy subjects were cocultured with RASFib.
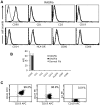
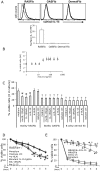
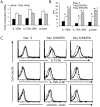
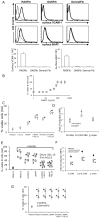
Results: RASFib constitutively expressed membrane IL-15. Survival of isolated B cells cultured for 6 days, below 5%, was extended in coculture with RASFib to 52+/-8% (p<0.001). IL-15 neutralizing agents but not isotype controls, reduced this rate to 31+/-6% (p<0.05). Interestingly, rhIL-15 had no effect on isolated B cells but significantly increased their survival in coculture with RASFib. In parallel, B cell IL-15R chains were upregulated in cocultures. BAFF and VCAM-1, that are expressed on RASFib, were tested as potential candidates involved in upregulating B cell IL-15R. Culture of B cells in the presence of rhBAFF or rhVCAM-1 resulted in significantly increased survival, together with upregulation of all three IL-15R chains; in parallel, rhIL-15 potentiated the anti-apoptotic effect of BAFF and VCAM-1. Both BAFF and VCAM-1 neutralizing agents downmodulated the effect of RASFib on B cell survival and IL-15R expression. In parallel, rhIL-15 had a lower effect on the survival of B cells cocultured with RASFib in the presence of BAFF or VCAM-1 neutralizing agents. Peripheral blood B cells from 15 early RA patients demonstrated an upregulated IL-15R and increased survival in cocultures.
Conclusion: IL-15 expression on RASFib significantly contributes to the anti-apoptotic effect of RASFib on B cells. IL-15 action is facilitated by BAFF and VCAM-1 expressed on RASFib, through an upregulation of IL-15R chains.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
A dual action of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblast IL-15 expression on the equilibrium between CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells and CD4+CD25- responder T cells.J Immunol. 2009 Dec 15;183(12):8268-79. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900007. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 20007590
-
Positive and negative cooperativity of TNF and Interferon-γ in regulating synovial fibroblast function and B cell survival in fibroblast/B cell co-cultures.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 21;10(1):780. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-57772-7. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31964950 Free PMC article.
-
IL-15 and the initiation of cell contact-dependent synovial fibroblast-T lymphocyte cross-talk in rheumatoid arthritis: effect of methotrexate.J Immunol. 2004 Jul 15;173(2):1463-76. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.2.1463. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15240743
-
Synoviocytes-derived Interleukin 35 Potentiates B Cell Response in Patients with Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2018 Apr;45(4):563-573. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.161363. Epub 2017 Dec 15. J Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29247146
-
[Rheumatoid arthritis: new developments in the pathogenesis with special reference to synovial fibroblasts].Z Rheumatol. 2001 Oct;60(5):309-18. doi: 10.1007/s003930170030. Z Rheumatol. 2001. PMID: 11759230 Review. German.
Cited by
-
New Developments in Transcriptomic Analysis of Synovial Tissue.Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Jan 31;7:21. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00021. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32083090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chlorogenic Acid Inhibits BAFF Expression in Collagen-Induced Arthritis and Human Synoviocyte MH7A Cells by Modulating the Activation of the NF-κB Signaling Pathway.J Immunol Res. 2019 May 22;2019:8042097. doi: 10.1155/2019/8042097. eCollection 2019. J Immunol Res. 2019. PMID: 31240234 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers predicting a need for intensive treatment in patients with early arthritis.Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(2):170-81. doi: 10.2174/1381612820666140825123104. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 25163741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of cytokine and chemokine expression by histone lysine methyltransferase MLL1 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts.Sci Rep. 2024 May 9;14(1):10610. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60860-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38719857 Free PMC article.
-
Redefinition of Synovial Fibroblasts in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Aging Dis. 2024 Jul 16;16(4):2054-2072. doi: 10.14336/AD.2024.0514. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 39122458 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zvaifler NJ, Boyle D, Firestein GS. Early synovitis–synoviocytes and mononuclear cells. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1994;23(6:11–16. - PubMed
-
- Weyand CM, Kang YM, Kurtin PJ, Goronzy JJ. The power of the third dimension: tissue architecture and autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003;15:259–266. - PubMed
-
- Cantaert T, Kolln J, Timmer T, van der Pouw Kraan TC, Vandooren B, et al. B lymphocyte autoimmunity in rheumatoid synovitis is independent of ectopic lymphoid neogenesis. J Immunol. 2008;181:785–794. - PubMed
-
- Zvaifler NJ. Rheumatoid synovitis. An extravascular immune complex disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1974;17:297–305. - PubMed
-
- Dörner T, Burmester GR. The role of B cells in rheumatoid arthritis: mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003;15:246–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

