Yersinia enterocolitica YopT and Clostridium difficile toxin B induce expression of GILZ in epithelial cells
- PMID: 22792400
- PMCID: PMC3392236
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040730
Yersinia enterocolitica YopT and Clostridium difficile toxin B induce expression of GILZ in epithelial cells
Abstract
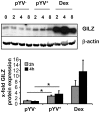
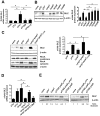
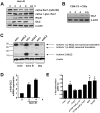
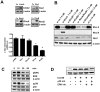
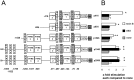
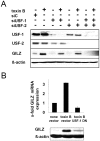
Glucocorticoid induced-leucine zipper (GILZ) has been shown to be induced in cells by different stimuli such as glucocorticoids, IL-10 or deprivation of IL-2. GILZ has anti-inflammatory properties and may be involved in signalling modulating apoptosis. Herein we demonstrate that wildtype Yersinia enterocolitica which carry the pYV plasmid upregulated GILZ mRNA levels and protein expression in epithelial cells. Infection of HeLa cells with different Yersinia mutant strains revealed that the protease activity of YopT, which cleaves the membrane-bound form of Rho GTPases was sufficient to induce GILZ expression. Similarly, Clostridium difficile toxin B, another bacterial inhibitor of Rho GTPases induced GILZ expression. YopT and toxin B both increased transcriptional activity of the GILZ promoter in HeLa cells. GILZ expression could not be linked to the inactivation of an individual Rho GTPase by these toxins. However, forced expression of RhoA and RhoB decreased basal GILZ promoter activity. Furthermore, MAPK activation proved necessary for profound GILZ induction by toxin B. Promoter studies and gel shift analyses defined binding of upstream stimulatory factor (USF) 1 and 2 to a canonical c-Myc binding site (E-box) in the GILZ promoter as a crucial step of its trans-activation. In addition we could show that USF-1 and USF-2 are essential for basal as well as toxin B induced GILZ expression. These findings define a novel way of GILZ promoter trans-activation mediated by bacterial toxins and differentiate it from those mediated by dexamethasone or deprivation of IL-2.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Smego RA, Frean J, Koornhof HJ. Yersiniosis I: microbiological and clinicoepidemiological aspects of plague and non-plague Yersinia infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1999;18:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Koornhof HJ, Smego RA, Jr, Nicol M. Yersiniosis. II: The pathogenesis of Yersinia infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1999;18:87–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

