Focus on Brain Angiotensin III and Aminopeptidase A in the Control of Hypertension
- PMID: 22792446
- PMCID: PMC3389720
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/124758
Focus on Brain Angiotensin III and Aminopeptidase A in the Control of Hypertension
Abstract
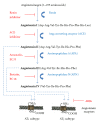
The classic renin-angiotensin system (RAS) was initially described as a hormone system designed to mediate cardiovascular and body water regulation. The discovery of a brain RAS composed of the necessary functional components (angiotensinogen, peptidases, angiotensins, and specific receptor proteins) independent of the peripheral system significantly expanded the possible physiological and pharmacological functions of this system. This paper first describes the enzymatic pathways resulting in active angiotensin ligands and their interaction with AT(1), AT(2), and mas receptor subtypes. Recent evidence points to important contributions by brain angiotensin III (AngIII) and aminopeptidases A (APA) and N (APN) in sustaining hypertension. Next, we discuss current approaches to the treatment of hypertension followed by novel strategies that focus on limiting the binding of AngII and AngIII to the AT(1) receptor subtype by influencing the activity of APA and APN. We conclude with thoughts concerning future treatment approaches to controlling hypertension and hypotension.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aminopeptidase A, which generates one of the main effector peptides of the brain renin-angiotensin system, angiotensin III, has a key role in central control of arterial blood pressure.Biochem Soc Trans. 2000;28(4):435-40. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000. PMID: 10961935 Review.
-
The brain renin-angiotensin system: a diversity of functions and implications for CNS diseases.Pflugers Arch. 2013 Jan;465(1):133-51. doi: 10.1007/s00424-012-1102-2. Epub 2012 Apr 26. Pflugers Arch. 2013. PMID: 22535332 Review.
-
Aminopeptidase A inhibitors as potential central antihypertensive agents.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Nov 9;96(23):13415-20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.23.13415. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10557335 Free PMC article.
-
Brain renin-angiotensin--a new look at an old system.Prog Neurobiol. 2011 Sep 15;95(1):49-67. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.07.001. Epub 2011 Jul 13. Prog Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21777652 Review.
-
[Identification of metabolic pathways of brain angiotensin II and angiotensin III: predominant role of angiotensin III in the control of vasopressin secretion].C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1998;192(4):607-18. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1998. PMID: 9842467 French.
Cited by
-
Aminopeptidases in Cardiovascular and Renal Function. Role as Predictive Renal Injury Biomarkers.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 5;21(16):5615. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165615. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32764495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atrial Fibrillation associated chromosome 4q25 variants are not associated with PITX2c expression in human adult left atrial appendages.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 22;9(1):e86245. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086245. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465984 Free PMC article.
-
Role of brain renin angiotensin system in neurodegeneration: An update.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020 Mar;27(3):905-912. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.01.026. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32127770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The relationship between chronic immune response and neurodegenerative damage in long COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 16;13:1039427. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1039427. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36591299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Counter-regulatory RAS peptides: new therapy targets for inflammation and fibrotic diseases?Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 10;15:1377113. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1377113. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38666016 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tigerstedt R, Bergman PG. Niere und Kreislauf. Scandinavian Archives of Physiology. 1898;8:223–271.
-
- Elliott DF, Peart WS. Amino-acid sequence in a hypertensin. Nature. 1956;177(4507):527–528. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous