A role for the cytoplasmic DEAD box helicase Dbp21E2 in rhodopsin maturation and photoreceptor viability
- PMID: 22794106
- PMCID: PMC3680124
- DOI: 10.3109/01677063.2012.692412
A role for the cytoplasmic DEAD box helicase Dbp21E2 in rhodopsin maturation and photoreceptor viability
Abstract
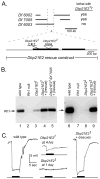
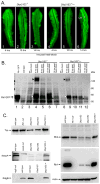
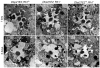
The Dbp21E2 (DEAD box protein 21E2) is a member of a family of DEAD box helicases active in RNA processing and stability. The authors used genetic mosaics to identify mutants in Dbp21E2 that affect rhodopsin biogenesis and the maintenance of photoreceptor structure. Analysis of a green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged Rh1 rhodopsin construct placed under control of a heat shock promoter showed that Dbp21E21 fails to efficiently transport Rh1 from the photoreceptor cell body to the rhabdomere. Retinal degeneration is not dependent on the Rh1 transport defects. The authors also showed that GFP- and red fluorescent protein (RFP)-tagged Dbp21E2 proteins are localized to discrete cytoplasmic structures that are not associated with organelles known to be active in rhodopsin transport. The molecular genetic analysis described here reveals an unexpected role for the Dbp21E2 helicase and provides an experimental system to further characterize its function.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Fluorescence-Based Genetic Screen to Study Retinal Degeneration in Drosophila.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 14;10(12):e0144925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144925. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26659849 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy-dependent rhodopsin degradation prevents retinal degeneration in Drosophila.J Neurosci. 2010 Aug 11;30(32):10703-19. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2061-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20702701 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila king tubby (ktub) mediates light-induced rhodopsin endocytosis and retinal degeneration.J Biomed Sci. 2012 Dec 10;19(1):101. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-19-101. J Biomed Sci. 2012. PMID: 23228091 Free PMC article.
-
Rhodopsin mutations as the cause of retinal degeneration. Classification of degeneration phenotypes in the model system Drosophila melanogaster.Acta Anat (Basel). 1998;162(2-3):85-94. doi: 10.1159/000046472. Acta Anat (Basel). 1998. PMID: 9831754 Review.
-
Molecular genetics of retinal degeneration: A Drosophila perspective.Fly (Austin). 2011 Oct-Dec;5(4):356-68. doi: 10.4161/fly.5.4.17809. Epub 2011 Sep 7. Fly (Austin). 2011. PMID: 21897116 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Fluorescent Proteins for Functional Dissection of the Drosophila Visual System.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 19;22(16):8930. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168930. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445636 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bier E, Vaessin H, Shepherd S, Lee K, McCall K, Barbel S, Ackerman L, Carretto R, Uemura T, Grell E, et al. Searching for pattern and mutation in the Drosophila genome with a P-lacZ vector. Genes & Development. 1989;3:1273–1287. - PubMed
-
- Brand AH, Perrimon N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development. 1993;118:401–415. - PubMed
-
- Caruthers JM, McKay DB. Helicase structure and mechanism. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2002;12:123–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
