Beige adipocytes are a distinct type of thermogenic fat cell in mouse and human
- PMID: 22796012
- PMCID: PMC3402601
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.016
Beige adipocytes are a distinct type of thermogenic fat cell in mouse and human
Abstract
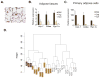
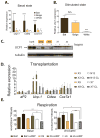
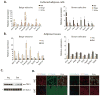
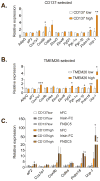
Brown fat generates heat via the mitochondrial uncoupling protein UCP1, defending against hypothermia and obesity. Recent data suggest that there are two distinct types of brown fat: classical brown fat derived from a myf-5 cellular lineage and UCP1-positive cells that emerge in white fat from a non-myf-5 lineage. Here, we report the isolation of "beige" cells from murine white fat depots. Beige cells resemble white fat cells in having extremely low basal expression of UCP1, but, like classical brown fat, they respond to cyclic AMP stimulation with high UCP1 expression and respiration rates. Beige cells have a gene expression pattern distinct from either white or brown fat and are preferentially sensitive to the polypeptide hormone irisin. Finally, we provide evidence that previously identified brown fat deposits in adult humans are composed of beige adipocytes. These data provide a foundation for studying this mammalian cell type with therapeutic potential. PAPERCLIP:
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Billon N, Dani C. Developmental Origins of the Adipocyte Lineage: New Insights from Genetics and Genomics Studies. Stem Cell Rev 2011 - PubMed
-
- Cinti S. Adipocyte differentiation and transdifferentiation: plasticity of the adipose organ. J Endocrinol Invest. 2002;25:823–835. - PubMed
-
- Collins S, Cao W, Robidoux J. Learning new tricks from old dogs: beta-adrenergic receptors teach new lessons on firing up adipose tissue metabolism. Mol Endocrinol. 2004;18:2123–2131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

