C3-heteroaroyl cannabinoids as photolabeling ligands for the CB2 cannabinoid receptor
- PMID: 22796181
- PMCID: PMC3445631
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.06.013
C3-heteroaroyl cannabinoids as photolabeling ligands for the CB2 cannabinoid receptor
Abstract
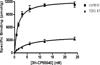
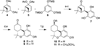
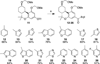
A series of tricyclic cannabinoids incorporating a heteroaroyl group at C3 were prepared as probes to explore the binding site(s) of the CB1 and CB2 receptors. This relatively unexplored structural motif is shown to be CB2 selective with K(i) values at low nanomolar concentrations when the heteroaromatic group is 3-benzothiophenyl (41) or 3-indolyl (50). When photoactivated, the lead compound 41 was shown to successfully label the CB2 receptor through covalent attachment at the active site while 50 failed to label. The benzothiophenone moiety may be a photoactivatable moiety suitable for selective labeling.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptor ligand specificity and the development of CB2-selective agonists.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(14):1428-43. doi: 10.2174/092986708784567716. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18537620 Review.
-
Highly Selective, Amine-Derived Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Probes.Chemistry. 2020 Jan 27;26(6):1380-1387. doi: 10.1002/chem.201904584. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Chemistry. 2020. PMID: 31961047
-
Synthesis and testing of novel classical cannabinoids: exploring the side chain ligand binding pocket of the CB1 and CB2 receptors.Bioorg Med Chem. 2003 Jul 17;11(14):3121-32. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(03)00238-4. Bioorg Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 12818675
-
CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptor binding studies based on modeling and mutagenesis approaches.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2005 Jul;5(7):651-8. doi: 10.2174/1389557054368754. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 16026311 Review.
-
Tricyclic Pyrazole-Based Compounds as Useful Scaffolds for Cannabinoid CB1/CB2 Receptor Interaction.Molecules. 2021 Apr 7;26(8):2126. doi: 10.3390/molecules26082126. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33917187 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel adamantyl cannabinoids as CB1 receptor probes.J Med Chem. 2013 May 23;56(10):3904-21. doi: 10.1021/jm4000775. Epub 2013 May 14. J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23621789 Free PMC article.
-
Novel analogs of PSNCBAM-1 as allosteric modulators of cannabinoid CB1 receptor.Bioorg Med Chem. 2017 Dec 15;25(24):6427-6434. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.10.015. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Bioorg Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 29079014 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping Cannabinoid 1 Receptor Allosteric Site(s): Critical Molecular Determinant and Signaling Profile of GAT100, a Novel, Potent, and Irreversibly Binding Probe.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2016 Jun 15;7(6):776-98. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.6b00041. Epub 2016 Apr 25. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27046127 Free PMC article.
-
Druggable Lipid Binding Sites in Pentameric Ligand-Gated Ion Channels and Transient Receptor Potential Channels.Front Physiol. 2022 Jan 4;12:798102. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.798102. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35069257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
2012 Division of medicinal chemistry award address. Trekking the cannabinoid road: a personal perspective.J Med Chem. 2014 May 22;57(10):3891-911. doi: 10.1021/jm500220s. Epub 2014 May 1. J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24707904 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Di Marzo V, Petrocellis LD. Ann. Rev. Med. 2006;57:553. - PubMed
-
- Compton DR, Prescott WR, Jr, Martin BR, Siegel C, Gordon PM, Razdan RK. J. Med. Chem. 1991;34:3310. - PubMed
-
- Martin BR, Jefferson R, Winckler R, Wiley JL, Huffman JW, Crocker PJ, Saha B, Razdan RK. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999;290:1065. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

