Future directions for cardiovascular disease comparative effectiveness research: report of a workshop sponsored by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
- PMID: 22796257
- PMCID: PMC3416944
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.12.057
Future directions for cardiovascular disease comparative effectiveness research: report of a workshop sponsored by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
Abstract
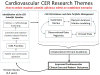
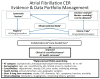
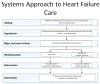
Comparative effectiveness research (CER) aims to provide decision makers with the evidence needed to evaluate the benefits and harms of alternative clinical management strategies. CER has become a national priority, with considerable new research funding allocated. Cardiovascular disease is a priority area for CER. This workshop report provides an overview of CER methods, with an emphasis on practical clinical trials and observational treatment comparisons. The report also details recommendations to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute for a new framework for evidence development to foster cardiovascular CER, and specific studies to address 8 clinical issues identified by the Institute of Medicine as high priorities for cardiovascular CER.
Copyright © 2012 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- IOM (Institute of Medicine) Initial national priorities for comparative effectiveness research. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 2009.
-
- Concato J, Peduzzi P, Huang G, O’Leary TJ, Kupersmith J. Comparative effectiveness research: What kind of studies do we need? J Investig Med. 2010;58:764–769. - PubMed
-
- The Atrial Fibrillation Follow-up Investigation of Rhythm Management (AFFIRM) Investigators. A comparison of rate control and rhythm control in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1825–1833. - PubMed
-
- The ALLHAT Officers and Coordinators for the ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. Major outcomes in high-risk hypertensive patients randomized to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or calcium channel blocker vs diuretic. The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT) JAMA. 2002;288:2981–2997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

