The NMDA receptor as a target for cognitive enhancement
- PMID: 22796429
- PMCID: PMC4696548
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.06.051
The NMDA receptor as a target for cognitive enhancement
Abstract
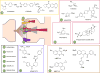
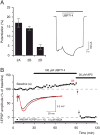
NMDA receptors (NMDARs) play an important role in neural plasticity including long-term potentiation and long-term depression, which are likely to explain their importance for learning and memory. Cognitive decline is a major problem facing an ageing human population, so much so that its reversal has become an important goal for scientific research and pharmaceutical development. Enhancement of NMDAR function is a core strategy toward this goal. In this review we indicate some of the major ways of potentiating NMDAR function by both direct and indirect modulation. There is good evidence that both positive and negative modulation can enhance function suggesting that a subtle approach correcting imbalances in particular clinical situations will be required. Excessive activation and the resultant deleterious effects will need to be carefully avoided. Finally we describe some novel positive allosteric modulators of NMDARs, with some subunit selectivity, and show initial evidence of their ability to affect NMDAR mediated events. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled 'Cognitive Enhancers'.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Abraham WC, Gustafsson B, Wigström H. Single high strength afferent volleys can produce long-term potentiation in the hippocampus in vitro. Neuroscience Letters. 1986;70:217–222. - PubMed
-
- Ali DW, Salter MW. NMDA receptor regulation by Src kinase signaling in excitatory synaptic transmission and plasticity. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2001;11:336–342. - PubMed
-
- Arai AC, Kessler M. Pharmacology of ampakine modulators: from AMPA receptors to synapses and behavior. Curr Drug Targets. 2007;8:583–602. - PubMed
-
- Arai A, Kessler M, Xiao P, Ambros-Ingerson J, Rogers G, Lynch G. A centrally active drug that modulates AMPA receptor gated currents. Brain Res. 1994;638:343–346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- G0601509/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0601813/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/F012519/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- G061812/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0601812/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

