Interference with RhoA-ROCK signaling mechanism in autoreactive CD4+ T cells enhances the bioavailability of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 22796435
- PMCID: PMC3432427
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.05.028
Interference with RhoA-ROCK signaling mechanism in autoreactive CD4+ T cells enhances the bioavailability of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
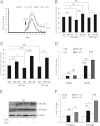
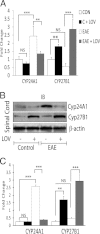
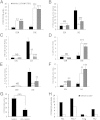
Vitamin D deficiency is a major risk factor for central nervous system (CNS) demyelinating diseases including multiple sclerosis (MS) and its animal model, that of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Both vitamin D(3) and 1, 25-dihydroxyviatmin-D(3) (calcitriol) had beneficial effects in EAE/MS. However, the exact cause of vitamin D deficiency in EAE/MS is not clear. Previously, we documented that lovastatin (LOV) provides protection in EAE animals via inhibition of RhoA-ROCK signaling. Herein, we demonstrate that LOV prevents the lowering of circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin-D(3) and 1,25-dihydroxyviatmin-D(3) levels including 1,25-dihydroxyviatmin-D(3) levels in the peripheral lymphoid organs and CNS of treated EAE animals. These effects of LOV were attributed to enhanced expression of vitamin D synthesizing enzyme (1α-hydroxylase) in kidney and the CNS, with corresponding reduction of vitamin D catabolizing enzyme (24-hydorxylase) expression in the CNS of EAE animals via inhibition of RhoA-ROCK signaling. Ex vivo and in vitro studies established that autoreactive Th1/Th17 cells had higher expression of 24-hydroxylase than Th2/T regulatory cells, that was reverted by LOV or ROCK inhibitor. Interestingly, LOV-mediated regulation of vitamin D metabolism had improved vitamin D(3) efficacy to confer protection in EAE animals and that was ascribed to the LOV- and calcitriol-induced immunomodulatory synergy. Together, these data provide evidence that interfering with RhoA-ROCK signaling in autoreactive Th1/Th17 cells can improve vitamin D(3) efficacy in clinical trials of MS and related neurodegenerative disorders.
Copyright © 2012 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Al-Omaishi J., Bashir R., Gendelman H.E. The cellular immunology of multiple sclerosis. J Leukoc Biol. 1999;65:444–452. - PubMed
-
- Prineas J.W., Barnard R.O., Kwon E.E., Sharer L.R., Cho E.S. Multiple sclerosis: remyelination of nascent lesions. Ann Neurol. 1993;33:137–151. - PubMed
-
- Bettelli E., Carrier Y., Gao W., Korn T., Strom T.B., Oukka M., Weiner H.L., Kuchroo V.K. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. 2006;441:235–238. - PubMed
-
- Marrie R.A. Environmental risk factors in multiple sclerosis aetiology. Lancet Neurol. 2004;3:709–718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

