Desmoglein 3 acting as an upstream regulator of Rho GTPases, Rac-1/Cdc42 in the regulation of actin organisation and dynamics
- PMID: 22796473
- PMCID: PMC4022105
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.07.002
Desmoglein 3 acting as an upstream regulator of Rho GTPases, Rac-1/Cdc42 in the regulation of actin organisation and dynamics
Abstract
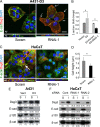
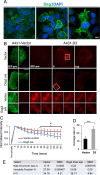
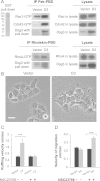
Desmoglein 3 (Dsg3), a member of the desmoglein sub-family, serves as an adhesion molecule in desmosomes. Our previous study showed that overexpression of human Dsg3 in several epithelial lines induces formation of membrane protrusions, a phenotype suggestive of Rho GTPase activation. Here we examined the interaction between Dsg3 and actin in detail and showed that endogenous Dsg3 colocalises and interacts with actin, particularly the junctional actin in a Rac1-dependent manner. Ablation of Rac1 activity by dominant negative Rac1 mutant (N17Rac1) or the Rac1 specific inhibitor (NSC23766) directly disrupts the interaction between Dsg3 and actin. Assembly of the junctional actin at the cell borders is accompanied with enhanced levels of Dsg3, while inhibition of Dsg3 by RNAi results in profound changes in the organisation of actin cytoskeleton. In accordance, overexpression of Dsg3 results in a remarkable increase of Rac1 and Cdc42 activities and to a lesser extent, RhoA. The enhancements in Rho GTPases are accompanied by the pronounced actin-based membrane structures such as lamellipodia and filopodia, enhanced rate of actin turnover and cell polarisation. Together, our results reveal an important novel function for Dsg3 in promoting actin dynamics through regulating Rac1 and Cdc42 activation in epithelial cells.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures







Similar articles
-
RhoA, Rac1, and Cdc42 exert distinct effects on epithelial barrier via selective structural and biochemical modulation of junctional proteins and F-actin.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004 Aug;287(2):C327-35. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00087.2004. Epub 2004 Mar 24. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15044152
-
Rac and Rho play opposing roles in the regulation of hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced permeability changes in pulmonary artery endothelial cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2005 Apr;288(4):L749-60. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00361.2004. Epub 2004 Dec 10. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15591411
-
DEF6, a novel PH-DH-like domain protein, is an upstream activator of the Rho GTPases Rac1, Cdc42, and RhoA.Exp Cell Res. 2004 Apr 1;294(2):335-44. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2003.12.004. Exp Cell Res. 2004. PMID: 15023524
-
FilGAP and its close relatives: a mediator of Rho-Rac antagonism that regulates cell morphology and migration.Biochem J. 2013 Jul 1;453(1):17-25. doi: 10.1042/BJ20130290. Biochem J. 2013. PMID: 23763313 Review.
-
The role of Rho GTPases' substrates Rac and Cdc42 in osteoclastogenesis and relevant natural medicinal products study.Biosci Rep. 2020 Jul 31;40(7):BSR20200407. doi: 10.1042/BSR20200407. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32578854 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Desmoglein-4 Deficiency Exacerbates Psoriasiform Dermatitis in Rats While Psoriasis Patients Displayed a Decreased Gene Expression of DSG4.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 29;12:625617. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.625617. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33995349 Free PMC article.
-
Desmoglein 3: a help or a hindrance in cancer progression?Cancers (Basel). 2015 Jan 26;7(1):266-86. doi: 10.3390/cancers7010266. Cancers (Basel). 2015. PMID: 25629808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of prostate smooth muscle contraction and prostate stromal cell growth by the inhibitors of Rac, NSC23766 and EHT1864.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jun;172(11):2905-17. doi: 10.1111/bph.13099. Epub 2015 May 5. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25631101 Free PMC article.
-
Immune response in pemphigus and beyond: progresses and emerging concepts.Semin Immunopathol. 2016 Jan;38(1):57-74. doi: 10.1007/s00281-015-0541-1. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Semin Immunopathol. 2016. PMID: 26597100 Review.
-
Cell adhesion in epidermal development and barrier formation.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015;112:383-414. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2014.11.027. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25733147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rudini N., Dejana E. Adherens junctions. Curr. Biol. 2008;18:R1080–R1082. - PubMed
-
- Etienne-Manneville S. Control of polarized cell morphology and motility by adherens junctions. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011;22:850–857. - PubMed
-
- Amagai M., Klaus-Kovtun V., Stanley J.R. Autoantibodies against a novel epithelial cadherin in pemphigus vulgaris, a disease of cell adhesion. Cell. 1991;67:869–877. - PubMed
-
- Amagai M., Ahmed A.R., Kitajima Y., Bystryn J.C., Milner Y., Gniadecki R., Hertl M., Pincelli C., Kurzen H., Fridkis-Hareli M., Aoyama Y., Frusic-Zlotkin M., Muller E., David M., Mimouni D., Vind-Kezunovic D., Michel B., Mahoney M., Grando S. Are desmoglein autoantibodies essential for the immunopathogenesis of pemphigus vulgaris, or just witnesses of disease? Exp. Dermatol. 2006;15:815–831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

