Role of matrix Gla protein in angiotensin II-induced exacerbation of vascular calcification
- PMID: 22796540
- PMCID: PMC3468471
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00826.2011
Role of matrix Gla protein in angiotensin II-induced exacerbation of vascular calcification
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016 Apr 1;310(7):H951. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.zh4-1873-corr.2016. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27036402 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
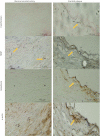
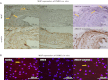
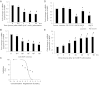
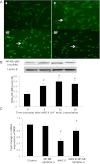
Vascular calcification predicts an increased risk for cardiovascular events in atherosclerosis, diabetes, and end-stage kidney diseases. Matrix Gla protein (MGP), an inhibitor of calcification, limits calcium phosphate deposition in the vessel wall. There are many factors contributing to the progression of atherosclerosis, including hypertension, hyperlipidemia, the renin-angiotensin system, and inflammation. Angiotensin II (ANG II) plays a crucial role in the atherogenic process through not only its pressor responses but also its growth-promoting and inflammatory effects. In this study, we investigated the role of MGP in ANG II-induced exacerbation of vascular calcification in human vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). The expression of MGP, calcification, and apoptosis in human VSMCs were examined by Western blot analysis, real-time PCR, in situ terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, respectively. Increase in VSMC calcification in human atherosclerotic plaques upregulates MGP expression and apoptosis in a negative feedback manner. ANG II inhibited MGP expression in VSMCs via and in vitro in a dose- and time-dependent manner through ANG II type 1 receptor and NF-κB signaling pathway. Meanwhile, MGP inhibited the calcification, caspase-3 activity, activation of runt-related transcription factor 2, and release of inflammatory cytokines by VSMCs induced by calcification medium (2.5 mM P(i)) and ANG II in vitro. These observations provide evidence that ANG II exacerbates vascular calcification through activation of the transcription factors, runt-related transcription factor 2 and NF-κB, and regulation of MGP, inflammatory cytokines expression in human VSMCs.
Figures



References
-
- Burdon KP, Rudock ME, Lehtinen AB, Langefeld CD, Bowden DW, Register TC, Liu Y, Freedman BI, Carr JJ, Hedrick CC, Rich SS. Human lipoxygenase pathway gene variation and association with markers of subclinical atherosclerosis in the diabetes heart study. Mediators Inflamm 2010: 170153, 2010 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hu WY, Fukuda N, Satoh C, Jian T, Kubo A, Nakayama M, Kishioka H, Kanmatsuse K. Phenotypic modulation by fibronectin enhances the angiotensin II-generating system in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20: 1500–1505, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Johnson RC, Leopold JA, Loscalzo J. Vascular calcification: pathobiological mechanisms and clinical implications. Circ Res 99: 1044–1059, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

