Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase alleviates high-glucose-induced dysfunction of brain microvascular endothelial cell tight-junction dynamics
- PMID: 22796592
- PMCID: PMC3437014
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.07.003
Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase alleviates high-glucose-induced dysfunction of brain microvascular endothelial cell tight-junction dynamics
Abstract
The blood-brain barrier, formed by specialized brain endothelial cells that are interconnected by tight junctions, strictly regulates paracellular permeability to maintain an optimal extracellular environment for brain homeostasis. Diabetes is known to compromise the blood-brain barrier, although the underlying mechanism remains unknown. The aim of this study was to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying disruption of the blood-brain barrier in diabetes and to determine whether activation of AMP-activated protein kinase prevents diabetes-induced blood-brain barrier dysfunction. Exposure of human brain microvascular endothelial cells to high glucose (25 mmol/L D-glucose), but not to high osmotic conditions (20 mmol/L L-glucose plus 5 mmol/L D-glucose), for 2h to 1 week significantly increased the permeability of the blood-brain barrier in parallel with lowered expression levels of zonula occludens-1, occludin, and claudin-5, three proteins that are essential to maintaining endothelial cell tight junctions. In addition, high glucose significantly increased the generation of superoxide anions. Adenoviral overexpression of superoxide dismutase or catalase significantly attenuated the high-glucose-induced reduction of endothelial cell tight-junction proteins. Furthermore, administration of apocynin reversed the effects of high glucose on endothelial cell tight-junction proteins. Finally, activation of AMP-activated protein kinase with 5-amino-4-imidazole carboxamide riboside or adenoviral overexpression of constitutively active AMP-activated protein kinase mutants abolished both the induction of NAD(P)H oxidase-derived superoxide anions and the tight-junction protein degradation induced by high glucose. We conclude that high glucose increases blood-brain barrier dysfunction in diabetes through induction of superoxide anions and that the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase protects the integrity of the blood-brain barrier by suppressing the induction of NAD(P)H oxidase-derived superoxide anions.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
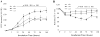
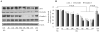





References
-
- Hawkins BT, Davis TP. The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2005;57:173–185. - PubMed
-
- Feldman GJ, Mullin JM, Ryan MP. Occludin: structure, function and regulation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005;57:883–917. - PubMed
-
- Krause G, Winkler L, Mueller SL, Haseloff RF, Piontek J, Blasig IE. Structure and function of claudins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1778:631–645. - PubMed
-
- Matter K, Balda MS. Signalling to and from tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:225–236. - PubMed
-
- Weiss N, Miller F, Cazaubon S, Couraud PO. The blood-brain barrier in brain homeostasis and neurological diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1788:842–857. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

