Nutritional immunity: transition metals at the pathogen-host interface
- PMID: 22796883
- PMCID: PMC3875331
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro2836
Nutritional immunity: transition metals at the pathogen-host interface
Abstract
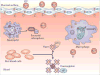
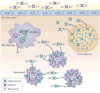
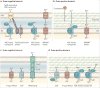
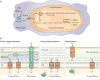
Transition metals occupy an essential niche in biological systems. Their electrostatic properties stabilize substrates or reaction intermediates in the active sites of enzymes, and their heightened reactivity is harnessed for catalysis. However, this heightened activity also renders transition metals toxic at high concentrations. Bacteria, like all living organisms, must regulate their intracellular levels of these elements to satisfy their physiological needs while avoiding harm. It is therefore not surprising that the host capitalizes on both the essentiality and toxicity of transition metals to defend against bacterial invaders. This Review discusses established and emerging paradigms in nutrient metal homeostasis at the pathogen-host interface.
Figures

References
-
- Andreini C, Bertini I, Cavallaro G, Holliday GL, Thornton JM. Metal ions in biological catalysis: from enzyme databases to general principles. Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry. 2008;13:1205–1218. - PubMed
-
- Andreini C, Bertini I, Rosato A. Metalloproteomes: a bioinformatic approach. Accounts of chemical research. 2009;42:1471–1479. - PubMed
-
- Andreini C, Banci L, Bertini I, Rosato A. Zinc through the three domains of life. Journal of Proteome Research. 2006;5:3173–3178. - PubMed
-
- Weinberg ED. Nutritional immunity. Host's attempt to withold iron from microbial invaders. Journal ofthe American Medical Association. 1975;231:39–41. - PubMed
-
- Weinberg ED. Iron availability and infection. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2009;1790:600–605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

