The mechanism of patellamide macrocyclization revealed by the characterization of the PatG macrocyclase domain
- PMID: 22796963
- PMCID: PMC3462482
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2340
The mechanism of patellamide macrocyclization revealed by the characterization of the PatG macrocyclase domain
Abstract
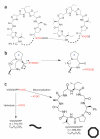
Peptide macrocycles are found in many biologically active natural products. Their versatility, resistance to proteolysis and ability to traverse membranes has made them desirable molecules. Although technologies exist to synthesize such compounds, the full extent of diversity found among natural macrocycles has yet to be achieved synthetically. Cyanobactins are ribosomal peptide macrocycles encompassing an extraordinarily diverse range of ring sizes, amino acids and chemical modifications. We report the structure, biochemical characterization and initial engineering of the PatG macrocyclase domain of Prochloron sp. from the patellamide pathway that catalyzes the macrocyclization of linear peptides. The enzyme contains insertions in the subtilisin fold to allow it to recognize a three-residue signature, bind substrate in a preorganized and unusual conformation, shield an acyl-enzyme intermediate from water and catalyze peptide bond formation. The ability to macrocyclize a broad range of nonactivated substrates has wide biotechnology applications.
Figures



References
-
- Blunt JW, Copp BR, Keyzers RA, Munro MH, Prinsep MR. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012;29:144–222. - PubMed
-
- Mayer AM, Rodriguez AD, Berlinck RG, Fusetani N. Marine pharmacology in 2007–8: marine compounds with antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; affecting the immune and nervous system, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011;153:191–222. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Driggers EM, Hale SP, Lee J, Terrett NK. The exploration of macrocycles for drug discovery–an underexploited structural class. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008;7:608–624. - PubMed
-
- Cuevas C, Francesch A. Development of Yondelis (trabectedin, ET-743). A semisynthetic process solves the supply problem. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009;26:322–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- 086036/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/H001212/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/H005447/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/F003439/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

