Inflammatory priming predisposes mice to age-related retinal degeneration
- PMID: 22797304
- PMCID: PMC3408755
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI64427
Inflammatory priming predisposes mice to age-related retinal degeneration
Abstract
Disruption of cellular processes affected by multiple genes and accumulation of numerous insults throughout life dictate the progression of age-related disorders, but their complex etiology is poorly understood. Postmitotic neurons, such as photoreceptor cells in the retina and epithelial cells in the adjacent retinal pigmented epithelium, are especially susceptible to cellular senescence, which contributes to age-related retinal degeneration (ARD). The multigenic and complex etiology of ARD in humans is reflected by the relative paucity of effective compounds for its early prevention and treatment. To understand the genetic differences that drive ARD pathogenesis, we studied A/J mice, which develop ARD more pronounced than that in other inbred mouse models. Although our investigation of consomic strains failed to identify a chromosome associated with the observed retinal deterioration, pathway analysis of RNA-Seq data from young mice prior to retinal pathological changes revealed that increased vulnerability to ARD in A/J mice was due to initially high levels of inflammatory factors and low levels of homeostatic neuroprotective factors. The genetic signatures of an uncompensated preinflammatory state and ARD progression identified here aid in understanding the susceptible genetic loci that underlie pathogenic mechanisms of age-associated disorders, including several human blinding diseases.
Figures

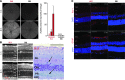
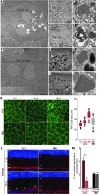

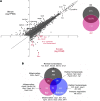

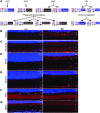

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 EY011373/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 EY007157/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY008061/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM007250/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P40 RR012305/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR12305/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32EY007157/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY11373/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 EY019880/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY019478/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY008061/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007250/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- EY019478/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- K08EY019880/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

