Identification of an Arabidopsis fatty alcohol:caffeoyl-Coenzyme A acyltransferase required for the synthesis of alkyl hydroxycinnamates in root waxes
- PMID: 22797656
- PMCID: PMC3440202
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.112.201822
Identification of an Arabidopsis fatty alcohol:caffeoyl-Coenzyme A acyltransferase required for the synthesis of alkyl hydroxycinnamates in root waxes
Abstract
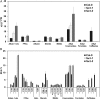
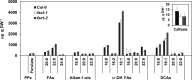
While suberin is an insoluble heteropolymer, a number of soluble lipids can be extracted by rapid chloroform dipping of roots. These extracts include esters of saturated long-chain primary alcohols and hydroxycinnamic acids. Such fatty alcohols and hydroxycinnamic acids are also present in suberin. We demonstrate that alkyl coumarates and caffeates, which are the major components of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) root waxes, are present primarily in taproots. Previously we identified ALIPHATIC SUBERIN FERULOYL TRANSFERASE (At5g41040), a HXXXD-type acyltransferase (BAHD family), responsible for incorporation of ferulate into aliphatic suberin of Arabidopsis. However, aliphatic suberin feruloyl transferase mutants were unaffected in alkyl hydroxycinnamate ester root wax composition. Here we identify a closely related gene, At5g63560, responsible for the synthesis of a subset of alkyl hydroxycinnamate esters, the alkyl caffeates. Transgenic plants harboring P(At5g63560)::YFP fusions showed transcriptional activity in suberized tissues. Knockout mutants of At5g63560 were severely reduced in their alkyl caffeate but not alkyl coumarate content. Recombinant At5g63560p had greater acyltransferase activity when presented with caffeoyl-Coenzyme A (CoA) substrate, thus we have named this acyltransferase FATTY ALCOHOL:CAFFEOYL-CoA CAFFEOYL TRANSFERASE. Stress experiments revealed elevated alkyl coumarate content in root waxes of NaCl-treated wild-type and fatty alcohol:caffeoyl-CoA caffeoyl transferase plants. We further demonstrate that FATTY ACYL-CoA REDUCTASEs (FARs) FAR5 (At3g44550), FAR4 (At3g44540), and FAR1 (At5g22500) are required for the synthesis of C18, C20, and C22 alkyl hydroxycinnamates, respectively. Collectively, these results suggest that multiple acyltransferases are utilized for the synthesis of alkyl hydroxycinnamate esters of Arabidopsis root waxes and that FAR1/4/5 provide the fatty alcohols required for alkyl hydroxycinnamate synthesis.
Figures







References
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al. (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Bechtold N, Ellis J, Pelletier G. (1993) In planta agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer by infiltration of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants. C R Acad Sci Paris Life Sci 316: 1194–1199
-
- Beisson F, Li-Beisson Y, Pollard M. (2012) Solving the puzzles of cutin and suberin polymer biosynthesis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 15: 329–337 - PubMed
-
- Bernards MA, Lewis NG. (1992) Alkyl ferulates in wound healing potato tubers. Phytochemistry 31: 3409–3412 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

