Meta-analysis identifies multiple loci associated with kidney function-related traits in east Asian populations
- PMID: 22797727
- PMCID: PMC4737645
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2352
Meta-analysis identifies multiple loci associated with kidney function-related traits in east Asian populations
Abstract
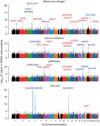
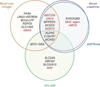
Chronic kidney disease (CKD), impairment of kidney function, is a serious public health problem, and the assessment of genetic factors influencing kidney function has substantial clinical relevance. Here, we report a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for kidney function-related traits, including 71,149 east Asian individuals from 18 studies in 11 population-, hospital- or family-based cohorts, conducted as part of the Asian Genetic Epidemiology Network (AGEN). Our meta-analysis identified 17 loci newly associated with kidney function-related traits, including the concentrations of blood urea nitrogen, uric acid and serum creatinine and estimated glomerular filtration rate based on serum creatinine levels (eGFRcrea) (P < 5.0 × 10(-8)). We further examined these loci with in silico replication in individuals of European ancestry from the KidneyGen, CKDGen and GUGC consortia, including a combined total of ∼110,347 individuals. We identify pleiotropic associations among these loci with kidney function-related traits and risk of CKD. These findings provide new insights into the genetics of kidney function.
Figures
References
-
- National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002;39:S1–S266. - PubMed
-
- Horio M, Imai E, Yasuda Y, Watanabe T, Matsuo S. Modification of the CKD epidemiology collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation for Japanese: accuracy and use for population estimates. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010;56:32–38. - PubMed
-
- Fox CS, et al. Genome-wide linkage analysis to serum creatinine, GFR, and creatinine clearance in a community-based population: the Framingham Heart Study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004;15:2457–2461. - PubMed
-
- Kamatani Y, et al. Genome-wide association study of hematological and biochemical traits in a Japanese population. Nat. Genet. 2010;42:210–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01HL087263/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UP_A100_1003/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01HL090682/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G1000143/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0401527/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01HL072507/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY014685/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0700931/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U127527198/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL087263/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL072507/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090682/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106188470/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

