Scale-up of HIV treatment through PEPFAR: a historic public health achievement
- PMID: 22797746
- PMCID: PMC3445041
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e31825eb27b
Scale-up of HIV treatment through PEPFAR: a historic public health achievement
Abstract
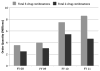
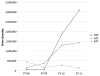
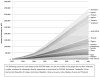
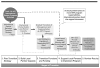
Since its inception in 2003, the US President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) has been an important driving force behind the global scale-up of HIV care and treatment services, particularly in expansion of access to antiretroviral therapy. Despite initial concerns about cost and feasibility, PEPFAR overcame challenges by leveraging and coordinating with other funders, by working in partnership with the most affected countries, by supporting local ownership, by using a public health approach, by supporting task-shifting strategies, and by paying attention to health systems strengthening. As of September 2011, PEPFAR directly supported initiation of antiretroviral therapy for 3.9 million people and provided care and support for nearly 13 million people. Benefits in terms of prevention of morbidity and mortality have been reaped by those receiving the services, with evidence of societal benefits beyond the anticipated clinical benefits. However, much remains to be accomplished to achieve universal access, to enhance the quality of programs, to ensure retention of patients in care, and to continue to strengthen health systems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no other funding or conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- WHO. Global HIV/AIDS Response: Epidemic Update and Health Sector Progress Towards Universal Access. Geneva, Switzerland: HIV/AIDS Department, World Health Organization; 2011.
-
- PEPFAR. [Accessed June 19, 2012];Using Science to Save Lives: Latest PEPFAR Results. 2011 Available at: http://www.pepfar.gov/documents/organization/187770.pdf.
-
- Dybul M. Lessons learned from PEPFAR. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2009;52(suppl 1):S12–S13. - PubMed
-
- PEPFAR. [Accessed: June 19, 2012];Five year partnership framework in support of the Tanzanian national response to HIV and AIDS, 2009–2012 between the government of the United Republic of Tanzania and the Government of the United States of America. Available at: http://www.pepfar.gov/frameworks/tanzania/139369.htm.
-
- Office of the US Global AIDS Coordinator. [Accessed June 19, 2012];PEPFAR: Making smart investments to increase impact and efficiency and save more lives. Available at: http://www.pepfar.gov/documents/organization/176783.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

