The chbG gene of the chitobiose (chb) operon of Escherichia coli encodes a chitooligosaccharide deacetylase
- PMID: 22797760
- PMCID: PMC3430350
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00533-12
The chbG gene of the chitobiose (chb) operon of Escherichia coli encodes a chitooligosaccharide deacetylase
Abstract
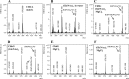
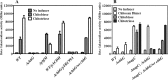
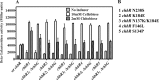
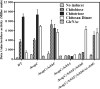
The chb operon of Escherichia coli is involved in the utilization of the β-glucosides chitobiose and cellobiose. The function of chbG (ydjC), the sixth open reading frame of the operon that codes for an evolutionarily conserved protein is unknown. We show that chbG encodes a monodeacetylase that is essential for growth on the acetylated chitooligosaccharides chitobiose and chitotriose but is dispensable for growth on cellobiose and chitosan dimer, the deacetylated form of chitobiose. The predicted active site of the enzyme was validated by demonstrating loss of function upon substitution of its putative metal-binding residues that are conserved across the YdjC family of proteins. We show that activation of the chb promoter by the regulatory protein ChbR is dependent on ChbG, suggesting that deacetylation of chitobiose-6-P and chitotriose-6-P is necessary for their recognition by ChbR as inducers. Strains carrying mutations in chbR conferring the ability to grow on both cellobiose and chitobiose are independent of chbG function for induction, suggesting that gain of function mutations in ChbR allow it to recognize the acetylated form of the oligosaccharides. ChbR-independent expression of the permease and phospho-β-glucosidase from a heterologous promoter did not support growth on both chitobiose and chitotriose in the absence of chbG, suggesting an additional role of chbG in the hydrolysis of chitooligosaccharides. The homologs of chbG in metazoans have been implicated in development and inflammatory diseases of the intestine, indicating that understanding the function of E. coli chbG has a broader significance.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of ChbG from Klebsiella pneumoniae reveals the molecular basis of diacetylchitobiose deacetylation.Commun Biol. 2022 Aug 24;5(1):862. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03824-9. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36002585 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the chitobiose operon of Escherichia coli is regulated by three transcription factors: NagC, ChbR and CAP.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Apr;52(2):437-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.03986.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15066032
-
Mutations that alter the regulation of the chb operon of Escherichia coli allow utilization of cellobiose.Mol Microbiol. 2007 Dec;66(6):1382-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05999.x. Epub 2007 Nov 19. Mol Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 18028317
-
Chitin, Chitin Oligosaccharide, and Chitin Disaccharide Metabolism of Escherichia coli Revisited: Reassignment of the Roles of ChiA, ChbR, ChbF, and ChbG.Microb Physiol. 2021;31(2):178-194. doi: 10.1159/000515178. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Microb Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33794535
-
A comparative study of the evolution of cellobiose utilization in Escherichia coli and Shigella sonnei.Arch Microbiol. 2017 Mar;199(2):247-257. doi: 10.1007/s00203-016-1299-0. Epub 2016 Oct 1. Arch Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 27695910
Cited by
-
Customized chitooligosaccharide production-controlling their length via engineering of rhizobial chitin synthases and the choice of expression system.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Dec 14;10:1073447. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1073447. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36588959 Free PMC article.
-
YdjC chitooligosaccharide deacetylase homolog induces keratin reorganization in lung cancer cells: involvement of interaction between YDJC and CDC16.Oncotarget. 2018 May 1;9(33):22915-22928. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25145. eCollection 2018 May 1. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29796162 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of ChbG from Klebsiella pneumoniae reveals the molecular basis of diacetylchitobiose deacetylation.Commun Biol. 2022 Aug 24;5(1):862. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03824-9. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36002585 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic diversity in Paenibacillus polymyxa: unveiling distinct species groups and functional variability.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jul 25;25(1):720. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10610-w. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39054421 Free PMC article.
-
N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) functions in cell signaling.Scientifica (Cairo). 2012 Jan 1;2012:489208. doi: 10.6064/2012/489208. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Scientifica (Cairo). 2012. PMID: 23350039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amann E, Ochs B, Abel KJ. 1988. Tightly regulated tac promoter vectors useful for the expression of unfused and fused proteins in Escherichia coli. Gene 69:301–315 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

