HLA-DR and HLA-DP restricted epitopes from human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B recognized by CD4+ T-cell clones from chronically infected individuals
- PMID: 22797815
- PMCID: PMC3528953
- DOI: 10.1007/s10875-012-9732-x
HLA-DR and HLA-DP restricted epitopes from human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B recognized by CD4+ T-cell clones from chronically infected individuals
Abstract
Purpose: Helper CD4(+) T cells presumably play a major role in controlling cytomegalovirus (CMV) by providing help to specific B and CD8(+) cytotoxic T cells, as well as through cytotoxicity-mediated mechanisms. Since CMV glycoprotein B (gB) is a major candidate for a subunit vaccine against CMV, we searched for gB-epitopes presented by human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-class II molecules.
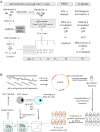
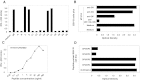
Methods: Dendritic cells obtained from CMV-seropositive donors were loaded with a recombinant gB and co-cultured with autologous CD4(+) T cells. Microcultures that specifically recognized gB were cloned by limiting dilution using autologous Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-immortalized B cells pulsed with gB as antigen-presenting cells. To pinpoint precisely the region encoding the natural epitope recognized by a given CD4(+) clone, we assessed the recognition of recombinant Escherichia coli expressing gB-overlapping polypeptides after their processing by autologous EBV-B cells.
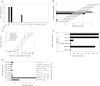
Results: We isolated several gB-specific CD4(+) T-cell clones directed against peptides gB(190-204), gB(396-410), gB(22-36) and gB(598-617) presented by HLA-DR7, HLA-DP10 and HLA-DP2. While their precise role in controlling CMV infection remains to be established, gB-specific CD4(+) T cells are likely to act by directly targeting infected HLA-class II cells in vivo, as suggested by their recognition of EBV-B cells infected by the Towne CMV strain.
Conclusions: The characterization of such gB-epitopes presented by HLA-class II should help to understand the contribution of CD4(+) T-cell responses to CMV and may be of importance both in designing a vaccine against CMV infection and in immunomonitoring of subjects immunized with recombinant gB or with vectors encoding gB.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Epitope-Specific CD4+ T Cells Are Inflated in HIV+ CMV+ Subjects.J Immunol. 2017 Nov 1;199(9):3187-3201. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700851. Epub 2017 Oct 2. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28972094 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of two T-cell epitopes on the candidate Epstein-Barr virus vaccine glycoprotein gp340 recognized by CD4+ T-cell clones.J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3821-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.65.7.3821-3828.1991. J Virol. 1991. PMID: 1710291 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-reactive recognition of human and primate cytomegalovirus sequences by human CD4 cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for glycoprotein B and H.Eur J Immunol. 2004 Nov;34(11):3216-26. doi: 10.1002/eji.200425203. Eur J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15368271
-
Refining human T-cell immunotherapy of cytomegalovirus disease: a mouse model with 'humanized' antigen presentation as a new preclinical study tool.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2016 Dec;205(6):549-561. doi: 10.1007/s00430-016-0471-0. Epub 2016 Aug 18. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27539576 Review.
-
Buffered memory: a hypothesis for the maintenance of functional, virus-specific CD8(+) T cells during cytomegalovirus infection.Immunol Res. 2011 Dec;51(2-3):195-204. doi: 10.1007/s12026-011-8251-9. Immunol Res. 2011. PMID: 22058020 Review.
Cited by
-
The Cellular Localization of Human Cytomegalovirus Glycoprotein Expression Greatly Influences the Frequency and Functional Phenotype of Specific CD4+ T Cell Responses.J Immunol. 2015 Oct 15;195(8):3803-15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500696. Epub 2015 Sep 11. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26363059 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Peptides identified on monocyte-derived dendritic cells: a marker for clinical immunogenicity to FVIII products.Blood Adv. 2019 May 14;3(9):1429-1440. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018030452. Blood Adv. 2019. PMID: 31053570 Free PMC article.
-
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Epitope-Specific CD4+ T Cells Are Inflated in HIV+ CMV+ Subjects.J Immunol. 2017 Nov 1;199(9):3187-3201. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700851. Epub 2017 Oct 2. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28972094 Free PMC article.
-
The human cytomegalovirus-encoded pUS28 antagonizes CD4+ T cell recognition by targeting CIITA.Elife. 2025 Jul 3;14:e96414. doi: 10.7554/eLife.96414. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40608405 Free PMC article.
-
AAV capsid CD8+ T-cell epitopes are highly conserved across AAV serotypes.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2015 Sep 30;2:15029. doi: 10.1038/mtm.2015.29. eCollection 2015. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2015. PMID: 26445723 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lilleri D, Zelini P, Fornara C, Comolli G, Revello MG, Gerna G. Human cytomegalovirus-specific CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell responses in primary infection of the immunocompetent and the immunocompromised host. Clin Immunol 2009 Mar 4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

