Combination delivery of TGF-β inhibitor and IL-2 by nanoscale liposomal polymeric gels enhances tumour immunotherapy
- PMID: 22797827
- PMCID: PMC3601683
- DOI: 10.1038/nmat3355
Combination delivery of TGF-β inhibitor and IL-2 by nanoscale liposomal polymeric gels enhances tumour immunotherapy
Abstract
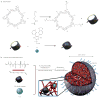
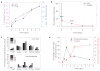
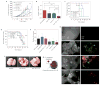
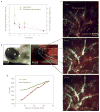
The tumour microenvironment thwarts conventional immunotherapy through multiple immunologic mechanisms, such as the secretion of the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), which stunts local tumour immune responses. Therefore, high doses of interleukin-2 (IL-2), a conventional cytokine for metastatic melanoma, induces only limited responses. To overcome the immunoinhibitory nature of the tumour microenvironment, we developed nanoscale liposomal polymeric gels (nanolipogels; nLGs) of drug-complexed cyclodextrins and cytokine-encapsulating biodegradable polymers that can deliver small hydrophobic molecular inhibitors and water-soluble protein cytokines in a sustained fashion to the tumour microenvironment. nLGs releasing TGF-β inhibitor and IL-2 significantly delayed tumour growth, increased survival of tumour-bearing mice, and increased the activity of natural killer cells and of intratumoral-activated CD8(+) T-cell infiltration. We demonstrate that the efficacy of nLGs in tumour immunotherapy results from a crucial mechanism involving activation of both innate and adaptive immune responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
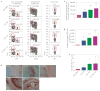
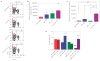
Comment in
-
Nanoparticle immunotherapy: Combo combat.Nat Mater. 2012 Oct;11(10):831-2. doi: 10.1038/nmat3434. Nat Mater. 2012. PMID: 23001226 No abstract available.
References
-
- Tawbi HA, Kirkwood JM. Management of metastatic melanoma. Semin Oncol. 2007;34:532–545. - PubMed
-
- Atkins MB, et al. High-dose recombinant interleukin 2 therapy for patients with metastatic melanoma: Analysis of 270 patients treated between 1985 and 1993. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2105–2116. - PubMed
-
- Acquavella N, et al. Toxicity and activity of a twice daily high-dose bolus interleukin 2 regimen in patients with metastatic melanoma and metastatic renal cell cancer. J Immunother. 2008;31:569–576. - PubMed
-
- Gorelik L, Flavell RA. Immune-mediated eradication of tumors through the blockade of transforming growth factor-β signaling in T cells. Nature Med. 2001;7:1118–1122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01-HL085416/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL112905/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P30 AR053495/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL-55397/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055397/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI082713/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085416/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-EB008260/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U19AI082713/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB008260/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P30AR053495/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

