Finding the weakest link: exploring integrin-mediated mechanical molecular pathways
- PMID: 22797926
- PMCID: PMC6518164
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.095794
Finding the weakest link: exploring integrin-mediated mechanical molecular pathways
Abstract
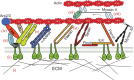
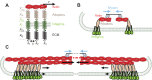
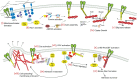
From the extracellular matrix to the cytoskeleton, a network of molecular links connects cells to their environment. Molecules in this network transmit and detect mechanical forces, which subsequently determine cell behavior and fate. Here, we reconstruct the mechanical pathway followed by these forces. From matrix proteins to actin through integrins and adaptor proteins, we review how forces affect the lifetime of bonds and stretch or alter the conformation of proteins, and how these mechanical changes are converted into biochemical signals in mechanotransduction events. We evaluate which of the proteins in the network can participate in mechanotransduction and which are simply responsible for transmitting forces in a dynamic network. Besides their individual properties, we also analyze how the mechanical responses of a protein are determined by their serial connections from the matrix to actin, their parallel connections in integrin clusters and by the rate at which force is applied to them. All these define mechanical molecular pathways in cells, which are emerging as key regulators of cell function alongside better studied biochemical pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanotransduction at focal adhesions: integrating cytoskeletal mechanics in migrating cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2013 Jun;17(6):704-12. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12054. Epub 2013 Apr 4. J Cell Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23551528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating actin dynamics, mechanotransduction and integrin activation: the multiple functions of actin binding proteins in focal adhesions.Eur J Cell Biol. 2013 Oct-Nov;92(10-11):339-48. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2013.10.009. Epub 2013 Nov 4. Eur J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24252517 Review.
-
Integrin-mediated mechanotransduction.J Cell Biol. 2016 Nov 21;215(4):445-456. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201609037. Epub 2016 Nov 8. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27872252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of mechanotransduction in integrin-mediated cell-matrix adhesion.Exp Cell Res. 2016 Nov 15;349(1):85-94. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.10.001. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Exp Cell Res. 2016. PMID: 27720950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focal adhesions as mechanosensors: the two-spring model.Biosystems. 2006 Feb-Mar;83(2-3):225-32. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2005.05.019. Epub 2005 Oct 19. Biosystems. 2006. PMID: 16236431
Cited by
-
DARC, Glycophorin A, Band 3, and GLUT1 Diffusion in Erythrocytes: Insights into Membrane Complexes.Biophys J. 2020 Nov 3;119(9):1749-1759. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.09.012. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 33069269 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the dystrophin glycoprotein complex in muscle cell mechanotransduction.Commun Biol. 2022 Sep 27;5(1):1022. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03980-y. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36168044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogels with Independently Controlled Adhesion Ligand Mobility and Viscoelasticity Increase Cell Adhesion and Spreading.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 24:2024.09.23.614501. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.23.614501. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39386463 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Mechanical control of nuclear import by Importin-7 is regulated by its dominant cargo YAP.Nat Commun. 2022 Mar 4;13(1):1174. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28693-y. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35246520 Free PMC article.
-
Integrins: Moonlighting Proteins in Invadosome Formation.Cancers (Basel). 2019 May 2;11(5):615. doi: 10.3390/cancers11050615. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31052560 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arnold M., Hirschfeld–Warneken V. C., Lohmüller T., Heil P., Blümmel J., Cavalcanti–Adam E. A., López–García M., Walther P., Kessler H., Geiger B.et al. (2008). Induction of cell polarization and migration by a gradient of nanoscale variations in adhesive ligand spacing. Nano Lett. 8, 2063–2069. 10.1021/nl801483w - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

