Extracellular loop cysteine mutant of cx37 fails to suppress proliferation of rat insulinoma cells
- PMID: 22797939
- PMCID: PMC3527626
- DOI: 10.1007/s00232-012-9459-x
Extracellular loop cysteine mutant of cx37 fails to suppress proliferation of rat insulinoma cells
Abstract
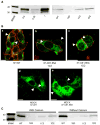
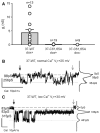
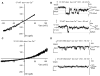
Although a functional pore domain is required for connexin 37 (Cx37)-mediated suppression of rat insulinoma (Rin) cell proliferation, it is unknown whether functional hemichannels would be sufficient or if Cx37 gap junction channels are required for growth suppression. To test this possibility, we targeted extracellular loop cysteines for mutation, expecting that the mutated protein would retain hemichannel, but not gap junction channel, functionality. Cysteines at positions 61 and 65 in the first extracellular loop of Cx37 were mutated to alanine and the mutant protein (Cx37-C61,65A) expressed in Rin cells. Although the resulting iRin37-C61,65A cells expressed the mutant protein comparably to Cx37 wild-type (Cx37-WT)--expressing Rin cells (iRin37), Cx37-C61,65A expression did not suppress the proliferation of Rin cells. As expected, iRin37-C61,65A cells did not form functional gap junction channels. However, functional hemichannels also could not be detected in iRin37-C61,65A cells by either dye uptake or electrophysiological approaches. Thus, failure of Cx37-C61,65A to suppress the proliferation of Rin cells is consistent with previous data demonstrating the importance of channel functionality to Cx37's growth-suppressive function. Moreover, failure of the Cx37-C61,65A hemichannel to function, even in low external calcium, emphasizes the importance of extracellular loop cysteines not only in hemichannel docking but also in determining the ability of the hemichannel to adopt a closed configuration that can open in response to triggers, such as low external calcium, effective at opening Cx37-WT hemichannels.
Figures
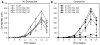


References
-
- Bao X, Chen Y, Reuss L, Altenberg GA. Functional expression in Xenopus oocytes of gap-junctional hemichannels formed by a cysteine-less connexin 43. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:9689–9692. - PubMed
-
- Beahm DL, Oshima A, Gaietta GM, Hand GM, Smock AE, Zucker SN, Toloue MM, Chandrasekhar A, Nicholson BJ, Sosinsky GE. Mutation of a conserved threonine in the third transmembrane helix of alpha- and beta-connexins creates a dominant-negative closed gap junction channel. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:7994–8009. - PubMed
-
- Bednarczyk D, Mash EA, Aavula BR, Wright SH. NBD-TMA: a novel fluorescent substrate of the peritubular organic cation transporter of renal proximal tubules. Pflugers Arch. 2000;440:184–192. - PubMed
-
- Burt JM, Fletcher AM, Steele TD, Wu Y, Cottrell GT, Kurjiaka DT. Alteration of Cx43:Cx40 expression ratio in A7r5 cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001;280:C500–C508. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

