Cardiac role of cyclic-GMP hydrolyzing phosphodiesterase type 5: from experimental models to clinical trials
- PMID: 22798047
- PMCID: PMC3408604
- DOI: 10.1007/s11897-012-0101-0
Cardiac role of cyclic-GMP hydrolyzing phosphodiesterase type 5: from experimental models to clinical trials
Abstract
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) and its primary signaling kinase, protein kinase G, play an important role in counterbalancing stress remodeling in the heart. Growing evidence supports a positive impact on a variety of cardiac disease conditions from the suppression of cGMP hydrolysis. The latter is regulated by members of the phosphodiesterase (PDE) superfamily, of which cGMP-selective PDE5 has been best studied. Inhibitors such as sildenafil and tadalafil ameliorate cardiac pressure and volume overload, ischemic injury, and cardiotoxicity. Clinical trials have begun exploring their potential to benefit dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. This review discusses recent developments in the field, highlighting basic science and clinical studies.
Figures
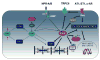
References
-
- Francis SH, Busch JL, Corbin JD, Sibley D. Cgmp-dependent protein kinases and cgmp phosphodiesterases in nitric oxide and cgmp action. Pharmacol Rev. 2010;62:525–563. This is an excellent review focusing on the molecular biology and biochemistry of the cGMP phosphodiesterases, and their signaling via PKG. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bender AT, Beavo JA. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: Molecular regulation to clinical use. Pharmacol Rev. 2006;58:488–520. - PubMed
-
- Zhang M, Kass DA. Phosphodiesterases and cardiac cgmp: Evolving roles and controversies. Trends in pharmacological sciences. 2011;32:360–365. This article discusses in particular the controversies surrounding which PDEs are most important to cardiac cGMP modulation in the heart, and the potential for this pathway to provide a novel therapeutic avenue. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

