Simultaneous onset of steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome and IDDM in two young children
- PMID: 22798086
- PMCID: PMC3030072
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr.04.2010.2916
Simultaneous onset of steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome and IDDM in two young children
Abstract
The cases are reported of two young children who developed insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) within 2 weeks of receiving a diagnosis of nephrotic syndrome. Neither patient responded to 8 weeks of daily prednisolone. The first patient presented at 2 years and 9 months of age. Her renal biopsy showed mesangial proliferation. The second child presented with steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome at 18 months of age and developed IDDM 2 weeks later. He achieved partial remission with cyclosporine therapy. His initial renal biopsy at 3 years of age showed minimal change disease and follow-up renal biopsy at 5 years of age showed early diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Tests for NPHS2 and WT1 genetic mutations were negative in both patients. To our knowledge this is the first report of steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome with almost simultaneous onset of IDDM in young children.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
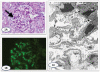
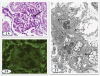
References
-
- Svensson M, Eriksson JW, Dahlquist G. Early glycemic control, age at onset and development of microvascular complications in childhood-onset type 1 diabetes: a population-based study in northern Sweden. Diabetes Care 2004;27:955–62 - PubMed
-
- Svensson M, Sundkvist G, Arnqvist HJ, et al. Signs of nephropathy may occur early in young adults with diabetes despite modern diabetes management: results from the nationwide population-based Diabetes Incidence Study in Sweden (DISS). Diabetes Care 2003;26:2903–9 - PubMed
-
- Pelliccia P, Savino A, Cecamore C, et al. Early changes in renal hemodynamics in children with diabetes: Doppler sonographic findings. J Clin Ultrasound 2008;36:335–40 - PubMed
-
- Raes A, Donckerwolcke R, Craen M, et al. Renal hemodynamic changes and renal functional reserve in children with type I diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Nephrol 2007;22:1903–9 - PubMed
-
- Agras PI, Kinik ST, Cengiz N, et al. Type 1 diabetes mellitus associated with nephrotic syndrome. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2006;19:1045–8 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
