The urban health transition hypothesis: empirical evidence of an avian influenza Kuznets curve in Vietnam?
- PMID: 22798150
- PMCID: PMC3675712
- DOI: 10.1007/s11524-012-9719-1
The urban health transition hypothesis: empirical evidence of an avian influenza Kuznets curve in Vietnam?
Abstract
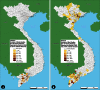
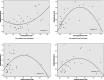
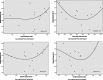
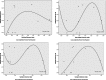
The literature on development has focused on the concept of transition in understanding the emergent challenges facing poor but rapidly developing countries. Scholars have focused extensively on the health and urban transitions associated with this change and, in particular, its use for understanding emerging infectious diseases. However, few have developed explicit empirical measures to quantify the extent to which a transitions focus is useful for theory, policy, and practice. Using open source data on avian influenza in 2004 and 2005 and the Vietnam Census of Population and Housing, this paper introduces the Kuznets curve as a tool for empirically estimating transition and disease. Findings suggest that the Kuznets curve is a viable tool for empirically assessing the role of transitional dynamics in the emergence of new infectious diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Perceived Risk of Avian Influenza and Urbanization in Northern Vietnam.Ecohealth. 2017 Mar;14(1):144-154. doi: 10.1007/s10393-017-1213-5. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Ecohealth. 2017. PMID: 28213653
-
Avian influenza H5N1 detected in poultry in Nigeria, further human cases reported in Iraq, Indonesia and China.Euro Surveill. 2006 Feb 9;11(2):E060209.1. Euro Surveill. 2006. PMID: 16804206 No abstract available.
-
Research suggests avian influenza may affect more humans than previously thought.Euro Surveill. 2006 Jan 12;11(1):E060112.2. Euro Surveill. 2006. PMID: 16801703 No abstract available.
-
Avian influenza virus H5N1: a review of its history and information regarding its potential to cause the next pandemic.Semin Pediatr Infect Dis. 2005 Oct;16(4):326-35. doi: 10.1053/j.spid.2005.07.002. Semin Pediatr Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 16210112 Review.
-
[The Cutting-edge of Medicine; A recent trend of emerging infections: MERS and Avian influenza A (H7N9)].Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi. 2015 Jan 10;104(1):114-9. doi: 10.2169/naika.104.114. Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi. 2015. PMID: 26571785 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Emerging infectious disease, the household built environment characteristics, and urban planning: Evidence on avian influenza in Vietnam.Landsc Urban Plan. 2020 Jan;193:103681. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2019.103681. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Landsc Urban Plan. 2020. PMID: 32287618 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for the Convergence Model: The Emergence of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (H5N1) in Viet Nam.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 23;10(9):e0138138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138138. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26398118 Free PMC article.
-
Perceived Risk of Avian Influenza and Urbanization in Northern Vietnam.Ecohealth. 2017 Mar;14(1):144-154. doi: 10.1007/s10393-017-1213-5. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Ecohealth. 2017. PMID: 28213653
-
Disentangling associations between vegetation greenness and dengue in a Latin American city: Findings and challenges.Landsc Urban Plan. 2021 Dec;216:None. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2021.104255. Landsc Urban Plan. 2021. PMID: 34675450 Free PMC article.
-
A landscape planning agenda for global health security: Learning from the history of HIV/AIDS and pandemic influenza.Landsc Urban Plan. 2021 Dec;216:104242. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2021.104242. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Landsc Urban Plan. 2021. PMID: 36536764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bunnell T. Kampung rules: landscape and the contested government of urban(e) Malayness. Urban Studies. 2002;39(9):1686–1701. doi: 10.1080/00420980220151727. - DOI
-
- Douglass M. From global intercity competition to cooperation for livable cities and economic resilience in Pacific Asia. Environ Urban. 2002;14(1):53–68. doi: 10.1177/095624780201400105. - DOI
-
- Friedmann J. China’s urban transition. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press; 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

