Glucocorticoid receptor and histone deacetylase-2 mediate dexamethasone-induced repression of MUC5AC gene expression
- PMID: 22798432
- PMCID: PMC3547101
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0009OC
Glucocorticoid receptor and histone deacetylase-2 mediate dexamethasone-induced repression of MUC5AC gene expression
Abstract
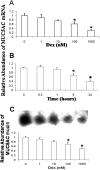
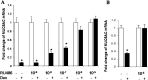
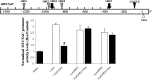
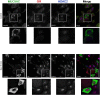
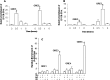
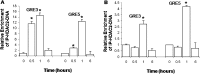
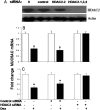
Airway occlusion in obstructive airway diseases is caused in part by the overproduction of secretory mucin glycoproteins through the up-regulation of mucin (MUC) genes by inflammatory mediators. Some pharmacological agents, including the glucocorticoid dexamethasone (Dex), repress mucin concentrations in lung epithelial cancer cells. Here, we show that Dex reduces the expression of MUC5AC, a major airway mucin gene, in primary differentiated normal human bronchial epithelial (NHBE) cells in a dose-dependent and time-dependent manner, and that the Dex-induced repression is mediated by the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and two glucocorticoid response elements (GREs) in the MUC5AC promoter. The pre-exposure of cells to RU486, a GR antagonist, and mutations in either the GRE3 or GRE5 cis-sites abolished the Dex-induced repression. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays showed a rapid temporal recruitment of GR to the GRE3 and GRE5 cis-elements in the MUC5AC promoter in NHBE and in A549 cells. Immunofluorescence showed nuclear colocalization of GR and histone deacetylase-2 (HDAC2) in MUC5AC-expressing NHBE cells. ChIP also showed a rapid temporal recruitment of HDAC2 to the GRE3 and GRE5 cis-elements in the MUC5AC promoter in both cell types. The knockdown of HDAC2 by HDAC2-specific short interfering RNA prevented the Dex-induced repression of MUC5AC in NHBE and A549 cells. These data demonstrate that GR and HDAC2 are recruited to the GRE3 and GRE5 cis-sites in the MUC5AC promoter and mediate the Dex-induced cis repression of MUC5AC gene expression. A better understanding of the mechanisms whereby glucocorticoids repress MUC5AC gene expression may be useful in formulating therapeutic interventions in chronic lung diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Rose MC. Mucins: structure, function, and role in pulmonary diseases. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 1992;263:L413–L429 - PubMed
-
- Corfield AP, Shukla AK. Mucins: vital components of the mucosal defensive barrier. Genom Proteom Technol 2003;3:20–22
-
- Rogers DF. Mucoactive agents for airway mucus hypersecretory diseases. Respir Care 2007;52:1176–1193 - PubMed
-
- Hollingsworth MA, Swanson BJ. Mucins in cancer: protection and control of the cell surface. Nat Rev Cancer 2004;4:45–60 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

