(E)-1-(2,4-Dinitro-phen-yl)-2-[1-(3-meth-oxy-phen-yl)ethyl-idene]hydrazine
- PMID: 22798819
- PMCID: PMC3393954
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812026979
(E)-1-(2,4-Dinitro-phen-yl)-2-[1-(3-meth-oxy-phen-yl)ethyl-idene]hydrazine
Abstract
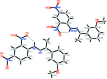
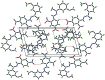
There are two crystallographically independent mol-ecules in the asymmetric unit of the title compound, C(15)H(14)N(4)O(5), with different conformations for the meth-oxy groups. The mol-ecules are both slightly twisted, the dihedral angles between two benzene rings being 8.37 (18)° in one and 7.31 (18)° in the other. In both mol-ecules, the two nitro groups are essentially coplanar with their bound benzene ring, with the r.m.s. deviation of the dinitro-benzene plane being 0.0310 (3) Å in one mol-ecule and 0.0650 (3) Å in the other. In each mol-ecule, an intra-molecular N-H⋯O hydrogen bond generates an S(6) ring motif. In the crystal, mol-ecules are linked by weak C-H⋯O inter-actions and stacked along the a axis through π-π inter-actions, with centroid-centroid distances of 3.651 (2) and 3.721 (2) Å. The crystal studied was a non-merohedral twin with a refined minor component of 20.1 (3)%.
Figures
Similar articles
-
(E)-1-(2,4-Dinitro-phen-yl)-2-[1-(3-nitro-phen-yl)ethyl-idene]hydrazine.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012 Sep 1;68(Pt 9):o2684-5. doi: 10.1107/S1600536812034812. Epub 2012 Aug 11. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012. PMID: 22969577 Free PMC article.
-
(E)-1-[1-(3-Chloro-phen-yl)ethyl-idene]-2-(2,4-dinitro-phen-yl)hydrazine.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012 Mar 1;68(Pt 3):o704-5. doi: 10.1107/S160053681200548X. Epub 2012 Feb 17. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012. PMID: 22412592 Free PMC article.
-
(E)-1-(2,4-Dinitro-phen-yl)-2-[1-(2-meth-oxy-phen-yl)ethyl-idene]hydrazine.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011 Dec 1;67(Pt 12):o3202-3. doi: 10.1107/S1600536811045417. Epub 2011 Nov 5. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011. PMID: 22199722 Free PMC article.
-
(E)-1-[1-(2-Chloro-phen-yl)ethyl-idene]-2-(2,4-dinitro-phen-yl)hydrazine.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011 Dec 1;67(Pt 12):o3499-500. doi: 10.1107/S160053681105001X. Epub 2011 Nov 30. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011. PMID: 22199971 Free PMC article.
-
1-[(Bromo-meth-yl)(phen-yl)meth-ylene]-2-(2,4-dinitro-phen-yl)hydrazine.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2009 May 7;65(Pt 6):o1221-2. doi: 10.1107/S1600536809016225. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2009. PMID: 21583090 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
1-(2,4-Di-nitro-phen-yl)-2-[(E)-2,4,5-tri-meth-oxy-benzyl-idene]hydrazine.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2013 Jul 6;69(Pt 8):o1203-4. doi: 10.1107/S1600536813018345. eCollection 2013. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2013. PMID: 24109301 Free PMC article.
-
1-(2,4-Di-nitro-phen-yl)-2-[(E)-(3,4,5-tri-meth-oxy-benzyl-idene)]hydrazine.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2014 Jan 22;70(Pt 2):o188-9. doi: 10.1107/S1600536814001238. eCollection 2014 Feb 1. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2014. PMID: 24764900 Free PMC article.
-
(E)-1-(2,4-Di-nitro-phen-yl)-2-(3-eth-oxy-4-hy-droxy-benzyl-idene)hydrazine.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2013 Dec 24;70(Pt 1):o89-90. doi: 10.1107/S1600536813033989. eCollection 2014 Jan 1. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2013. PMID: 24527018 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure and Hirshfeld surface analysis of (E)-1-(2,6-di-chloro-phen-yl)-2-(2-nitro-benzyl-idene)hydrazine.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2020 Jul 3;76(Pt 8):1173-1178. doi: 10.1107/S2056989020008567. eCollection 2020 Aug 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2020. PMID: 32843995 Free PMC article.
-
(E)-1-(2,6-Di-chloro-phen-yl)-2-(3-nitro-benzyl-idene)hydrazine: crystal structure and Hirshfeld surface analysis.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2020 Jul 17;76(Pt 8):1291-1295. doi: 10.1107/S2056989020009433. eCollection 2020 Aug 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2020. PMID: 32844016 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
-
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
-
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
