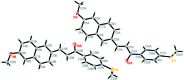
(2E)-3-(6-Meth-oxy-naphthalen-2-yl)-1-[4-(methyl-sulfan-yl)phen-yl]prop-2-en-1-one
- PMID: 22798922
- PMCID: PMC3394057
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812028930
(2E)-3-(6-Meth-oxy-naphthalen-2-yl)-1-[4-(methyl-sulfan-yl)phen-yl]prop-2-en-1-one
Abstract
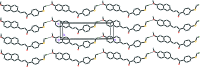
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, C(21)H(18)O(2)S, consists of two crystallographically independent mol-ecules (A and B). The mol-ecules exist in a trans conformation with respect to the central C=C bond. The naphthalene ring system makes dihedral angles of 51.62 (12) (mol-ecule A) and 52.69 (12)° (mol-ecule B) with the benzene ring. In mol-ecule A, the prop-2-en-1-one group forms dihedral angles of 22.84 (15) and 29.02 (12)° with the adjacent naphthalene ring system and benzene ring, respectively, whereas the corresponding angles are 30.04 (12) and 23.33 (12)° in mol-ecule B. In the crystal, mol-ecules are linked by inter-molecular C-H⋯O hydrogen bonds into head-to-tail chains along the a axis. The crystal packing also features C-H⋯π inter-actions. The crystal studied was a pseudo-merohedral twin with twin law (100 0-10 00-1) and a refined component ratio of 0.6103 (16):0.3897 (16).
Figures
Similar articles
-
(E)-1-(2-Amino-phen-yl)-3-(3,4,5-trimeth-oxy-phen-yl)prop-2-en-1-one.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011 Sep 1;67(Pt 9):o2485-6. doi: 10.1107/S1600536811033861. Epub 2011 Aug 27. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011. PMID: 22064816 Free PMC article.
-
(E)-1-(4-Amino-phen-yl)-3-(naphthalen-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011 May 1;67(Pt 5):o1204-5. doi: 10.1107/S1600536811014024. Epub 2011 Apr 22. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011. PMID: 21754504 Free PMC article.
-
Three closely related (2E,2'E)-3,3'-(1,4-phenyl-ene)bis-[1-(meth-oxy-phen-yl)prop-2-en-1-ones]: supra-molecular assemblies in one dimension mediated by hydrogen bonding and C-H⋯π inter-actions.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2017 May 26;73(Pt 6):896-900. doi: 10.1107/S2056989017007460. eCollection 2017 Jun 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2017. PMID: 28638654 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of (2E)-1-(3-bromo-thio-phen-2-yl)-3-(2-meth-oxy-phen-yl)prop-2-en-1-one and (2E)-1-(3-bromo-thio-phen-2-yl)-3-(3,4-di-meth-oxy-phen-yl)prop-2-en-1-one.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2015 Jul 25;71(Pt 8):965-71. doi: 10.1107/S2056989015013420. eCollection 2015 Aug 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2015. PMID: 26396767 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of (E)-3-(3,4-di-meth-oxy-phen-yl)-1-(1-hy-droxy-naphthalen-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2015 Apr 30;71(Pt 5):o371-2. doi: 10.1107/S2056989015008087. eCollection 2015 May 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2015. PMID: 25995955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
-
- Amir, M., Javed, S. A. & Kumar, H. (2008). Acta Pharm. 58, 467–477. - PubMed
-
- Atwal, K. S., Rovnyak, G. C., Kimball, S. D., Floyd, D. M., Moreland, S., Swanson, B. N., Gougoutas, J. Z., Schwartz, J., Smillie, K. M. & Malley, M. F. (1990). J. Med. Chem. 33, 2629–2635. - PubMed
-
- Bruker (2009). SADABS, APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Cosier, J. & Glazer, A. M. (1986). J. Appl. Cryst. 19, 105–107.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials