High definition spectral domain optical coherence tomography findings in three patients with solar retinopathy and review of the literature
- PMID: 22798967
- PMCID: PMC3394112
- DOI: 10.2174/1874364101206010029
High definition spectral domain optical coherence tomography findings in three patients with solar retinopathy and review of the literature
Abstract
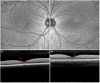
Purpose: To describe ocular findings in 3 cases of solar retinopathy using high definition, spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) and review the literature for optical coherence tomography (OCT) characteristics associated with worse vision.
Methods: Case series and retrospective review of clinical features and Spectralis SD-OCT (Heidelberg Engineering, Vista, California, United States of America). A literature review of OCT findings in cases of solar retinopathy reported on MEDLINE was also performed and analyzed.
Results: Six eyes of 3 patients with solar retinopathy revealed significant foveal pathology. Visual acuity ranged from Snellen 20/30 to 20/50. High definition SD-OCT demonstrated defects at the level of the inner and outer segment junction of the photoreceptors as well as in the inner high reflective layer. There was a significant correlation between chronic disruption of the inner photoreceptor junction with worse vision based on the current case series and literature review.
Conclusions: Screening patients with exposure to central foveal damage from solar retinopathy with high definition SD-OCT improves diagnosis and assessment of photoreceptor damage and vision loss.
Keywords: Solar retinopathy; Spectralis SD-OCT.; fovea; spectral domain optical coherence tomography.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of spectral-domain and time-domain optical coherence tomography in solar retinopathy.Korean J Ophthalmol. 2011 Aug;25(4):278-81. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2011.25.4.278. Epub 2011 Jul 22. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 21860577 Free PMC article.
-
Solar retinopathy: comparison of optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fluorescein angiography (FA).Retina. 2009 Oct;29(9):1340-5. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e3181b0da88. Retina. 2009. PMID: 19934824
-
Solar retinopathy-correlation between adaptive optics and spectral domain optical coherence tomography with visual acuity.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2021 May;259(5):1161-1166. doi: 10.1007/s00417-020-04961-9. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33044593
-
Morphologic photoreceptor abnormality in occult macular dystrophy on spectral-domain optical coherence tomography.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Jul;51(7):3673-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-4169. Epub 2010 Feb 17. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 20164460
-
Solar retinopathy: A literature review.Oman J Ophthalmol. 2024 Jun 27;17(2):173-180. doi: 10.4103/ojo.ojo_248_23. eCollection 2024 May-Aug. Oman J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39132123 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Is the mechanism of 'poppers maculopathy' photic injury?Eye (Lond). 2013 Dec;27(12):1420-1. doi: 10.1038/eye.2013.218. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Eye (Lond). 2013. PMID: 24113304 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Multimodal imaging of a patient with poppers maculopathy.GMS Ophthalmol Cases. 2020 Apr 2;10:Doc16. doi: 10.3205/oc000143. eCollection 2020. GMS Ophthalmol Cases. 2020. PMID: 32676261 Free PMC article.
-
Solar maculopathy: prognosis over one year follow up.BMC Ophthalmol. 2019 Sep 18;19(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s12886-019-1199-6. BMC Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31533669 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term anatomical and functional findings of solar maculopathy.Ir J Med Sci. 2024 Feb;193(1):435-441. doi: 10.1007/s11845-023-03434-2. Epub 2023 Jun 29. Ir J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 37380832 Review.
-
Multimodal Imaging and Macular Hyalocyte Count in a Patient with Acute Macular Neuroretinopathy.Case Rep Ophthalmol Med. 2022 Oct 25;2022:2855191. doi: 10.1155/2022/2855191. eCollection 2022. Case Rep Ophthalmol Med. 2022. PMID: 36329692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gass JDM. Stereoscopic atlas of macular diseases: diagnosis and treatment. 4th. St. Louis: Mosby; 1997. pp. 760–3.
-
- Codenotti M, Patelli M, Brancato R. OCT Findings in patients with retinopathy after watching a solar eclipse. Ophthalmologica. 2002;216(6 ):463–6. - PubMed
-
- Jain A, Desai RU, Charalel RA, et al. Solar retinopathy comparison of optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fluorescein angiography (FA) Retina. 2009;29(9 ):340–5. - PubMed
-
- Tso MO, La Piana FG. The human fovea after sungazing. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1975;79(6 ):788–95. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
