Cytomolecular characterization of de novo formed rye B chromosome variants
- PMID: 22800712
- PMCID: PMC3541114
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-8166-5-34
Cytomolecular characterization of de novo formed rye B chromosome variants
Abstract
Background: B chromosomes (Bs) are dispensable elements which occur in many species including rye (Secale cereale). We determined the organization of B variants to obtain insights into the origin of B polymorphisms in rye.
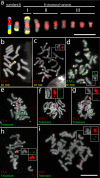
Results: The observed B variants were classified according to their morphology and in situ hybridization patterns with the B-specific repeats D1100 and CL11 into (I) long arm iso B, (II) D1100-deficient B and (III) small metacentric B variants. Long arm iso Bs are likely products of a meiotic centromere misdivision and subsequent duplication of the long arm, whereas small B variants are probably generated by chromosome breakage. Some deficient Bs experienced extensive amplification of CL11 repeats.
Conclusions: Both the pericentromere and the nondisjunction control region seem to be involved in the generation of rye B chromosome variants. However, due to the loss of the B-specific nondisjuction control region most of the variants generated are not capable to accumulate in a population.
Figures
Similar articles
-
B chromosomes of rye are highly conserved and accompanied the development of early agriculture.Ann Bot. 2013 Aug;112(3):527-34. doi: 10.1093/aob/mct121. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Ann Bot. 2013. PMID: 23739836 Free PMC article.
-
Nature and evolution of B chromosomes in plants: A non-coding but information-rich part of plant genomes.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2002;96(1-4):198-205. doi: 10.1159/000063047. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2002. PMID: 12438799
-
The centromere structure in Robertsonian wheat-rye translocation chromosomes indicates that centric breakage-fusion can occur at different positions within the primary constriction.Chromosoma. 2001 Sep;110(5):335-44. doi: 10.1007/s004120100159. Chromosoma. 2001. PMID: 11685533
-
Chromosomes with a life of their own.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2008;120(3-4):265-80. doi: 10.1159/000121076. Epub 2008 May 23. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2008. PMID: 18504356 Review.
-
Progress on molecular composition and genetic mechanism of plant B chromosomes.Yi Chuan. 2022 Sep 20;44(9):772-782. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-116. Yi Chuan. 2022. PMID: 36384954 Review.
Cited by
-
Rye (Secale cereale) supernumerary (B) chromosomes associated with heat tolerance during early stages of male sporogenesis.Ann Bot. 2017 Feb;119(3):325-337. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcw206. Epub 2016 Nov 5. Ann Bot. 2017. PMID: 27818381 Free PMC article.
-
B chromosomes of rye are highly conserved and accompanied the development of early agriculture.Ann Bot. 2013 Aug;112(3):527-34. doi: 10.1093/aob/mct121. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Ann Bot. 2013. PMID: 23739836 Free PMC article.
-
Satellite DNAs Unveil Clues about the Ancestry and Composition of B Chromosomes in Three Grasshopper Species.Genes (Basel). 2018 Oct 26;9(11):523. doi: 10.3390/genes9110523. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30373193 Free PMC article.
-
Out of patterns, the euchromatic B chromosome of the grasshopper Abracris flavolineata is not enriched in high-copy repeats.Heredity (Edinb). 2021 Nov;127(5):475-483. doi: 10.1038/s41437-021-00470-5. Epub 2021 Sep 4. Heredity (Edinb). 2021. PMID: 34482369 Free PMC article.
-
Organization of some repetitive DNAs and B chromosomes in the grasshopper Eumastusia koebelei koebelei (Rehn, 1909) (Orthoptera, Acrididae, Leptysminae).Comp Cytogenet. 2016 Apr 6;10(2):219-28. doi: 10.3897/CompCytogen.v10i2.7609. eCollection 2016. Comp Cytogenet. 2016. PMID: 27551344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilson EB. The supernumerary chromosomes of Hemiptera. Science. 1907;26:870–871.
-
- Houben A, Thompson N, Ahne R, Leach CR, Verlin D, Timmis JN. A monophyletic origin of the B chromosomes of Brachycome dichromosomatica (Asteraceae) Plant Syst Evol. 1999;219:127–135. doi: 10.1007/BF01090304. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

