Complement C1q formation of immune complexes with milk caseins and wheat glutens in schizophrenia
- PMID: 22801085
- PMCID: PMC3465075
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.07.005
Complement C1q formation of immune complexes with milk caseins and wheat glutens in schizophrenia
Abstract
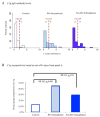
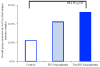
Immune system factors including complement pathway activation are increasingly linked to the etiology and pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Complement protein, C1q, binds to and helps to clear immune complexes composed of immunoglobulins coupled to antigens. The antigenic stimuli for C1q activation in schizophrenia are not known. Food sensitivities characterized by elevated IgG antibodies to bovine milk caseins and wheat glutens have been reported in individuals with schizophrenia. Here, we examined the extent to which these food products might comprise the antigen component of complement C1q immune complexes in individuals with recent onset schizophrenia (n=38), non-recent onset schizophrenia (n=61) and non-psychiatric controls (n=63). C1q seropositivity was significantly associated with both schizophrenia groups (recent onset, odds ratio (OR)=8.02, p≤0.008; non-recent onset, OR=3.15, p≤0.03) compared to controls (logistic regression models corrected for age, sex, race and smoking status). Casein- and/or gluten-IgG binding to C1q was significantly elevated in the non-recent onset group compared to controls (OR=4.36, p≤0.01). Significant amounts of C1q-casein/gluten-related immune complexes and C1q correlations with a marker for gastrointestinal inflammation in non-recent onset schizophrenia suggests a heightened rate of food antigens in the systemic circulation, perhaps via a disease-associated altered intestinal permeability. In individuals who are in the early stages of disease onset, C1q activation may reflect the formation of immune complexes with non-casein- or non-gluten-related antigens, the presence of C1q autoantibodies, and/or a dissociated state of immune complex components. In conclusion, complement activation may be a useful biomarker to diagnose schizophrenia early during the course of the disease. Future prospective studies should evaluate the impacts of casein- and gluten-free diets on C1q activation in schizophrenia.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Benros ME, Nielsen PR, Nordentoft M, Eaton WW, Dalton SO, Mortensen PB. Autoimmune diseases and severe infections as risk factors for schizophrenia: A 30-year population-based register study. Am J Psychiatry. 2011;168:1303–10. - PubMed
-
- Boulanger LM. Immune proteins in brain development and synaptic plasticity. Neuron. 2009;64:93–109. - PubMed
-
- Boyajyan A, Khoyetsyan A, Tsakanova G, Sim RB. Cryoglobulins as indicators of upregulated immune response in schizophrenia. Clin Biochem. 2008;41:355–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

