Anticonvulsant and antiarrhythmic effects of nifedipine in rats prone to audiogenic seizures
- PMID: 22801414
- PMCID: PMC3854160
- DOI: 10.1590/s0100-879x2012007500119
Anticonvulsant and antiarrhythmic effects of nifedipine in rats prone to audiogenic seizures
Abstract
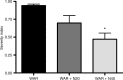
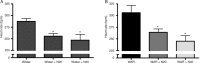
Calcium ion participates in the regulation of neural transmission and the presynaptic release of neurotransmitters. It is also involved in epileptic events, cardiac arrhythmias and abnormal conduction of stimuli. The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the effects of nifedipine, a calcium channel blocker, on epileptic seizures and on reperfusion arrhythmias in rats prone to audiogenic epileptic seizures (Wistar audiogenic rats, WAR) and in normal Wistar rats (N = 6/group). The seizure severity index was applied after an intraperitoneal injection of 20 or 40 mg/kg nifedipine (N20 and N40 groups, respectively). The Langendorff technique was used to analyze cardiac function, as well as the incidence and severity of the reperfusion arrhythmias after ligature and release of the left coronary artery in rats treated or not with nifedipine. We found that nifedipine treatment decreased seizure severity (0.94 ± 0.02 for WAR; 0.70 ± 0.10 for WAR + N20; 0.47 ± 0.08 for WAR + N40) and increased the latent period (13 ± 2 s for WAR; 35 ± 10 s for WAR + N20; 48 ± 7 s for WAR + N40) for the development of seizures in WAR. Furthermore, the incidence and severity of the reperfusion arrhythmias were lower in WAR and normal Wistar rats injected with nifedipine. In WAR, these effects were mediated, at least in part, by a decrease in heart rate. Thus, our results indicate that nifedipine may be considered to be a potential adjuvant drug for epilepsy treatment, especially in those cases associated with cardiac rhythm abnormalities.
Figures

References
-
- Theodore WH, Spencer SS, Wiebe S, Langfitt JT, Ali A, Shafer PO, et al. Epilepsy in North America: a report prepared under the auspices of the global campaign against epilepsy, the International Bureau for Epilepsy, the International League Against Epilepsy, and the World Health Organization. Epilepsia. 2006;47:1700–1722. - PubMed
-
- Ansakorpi H, Korpelainen JT, Suominen K, Tolonen U, Myllyla VV, Isojarvi JI. Interictal cardiovascular autonomic responses in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2000;41:42–47. - PubMed
-
- Nei M, Ho RT, Sperling MR. EKG abnormalities during partial seizures in refractory epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2000;41:542–548. - PubMed
-
- Cockerell OC, Johnson AL, Sander JW, Hart YM, Goodridge DM, Shorvon SD. Mortality from epilepsy: results from a prospective population-based study. Lancet. 1994;344:918–921. - PubMed
-
- Opherk C, Coromilas J, Hirsch LJ. Heart rate and EKG changes in 102 seizures: analysis of influencing factors. Epilepsy Res. 2002;52:117–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

